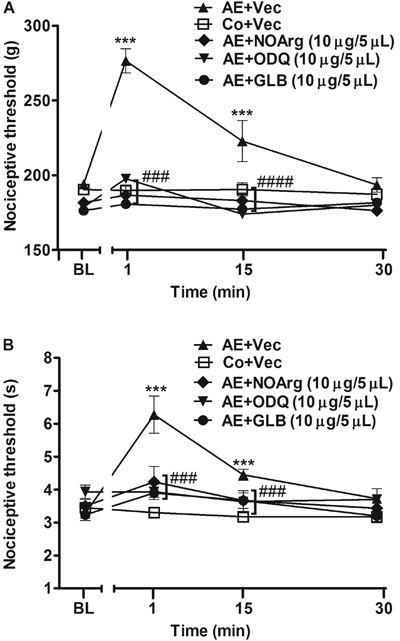
Figure 3. Effect of intracerebroventricular administration of nitric oxide/cGMP/KATP pathway inhibitors on the antinociception induced by acute aerobic exercise (AE) in the paw-withdrawal (A) and tail-flick (B) tests. Rats were pretreated with intracerebroventricular injection of N-nitro-L-arginine (L-NOArg, 10 μg/5 µL), H-(1,2,4)oxidiazolo[4,3-a]quinoxalin-1-one (ODQ, 10 μg/5 µL) and glibenclamide (GLB, 10 μg/5 µL) immediately before the onset of exercise, which lasted for a mean of 44.2±1.5 min. Mechanical and thermal nociceptive thresholds were measured before and after 1, 15, 30 min of AE. Data are reported as means±SE of 6 animals per group. ***P<0.001, compared to the control group (Co); ###P<0.001, compared to the AE group (one-way ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni test). Vec: vehicle; BL: baseline latency.