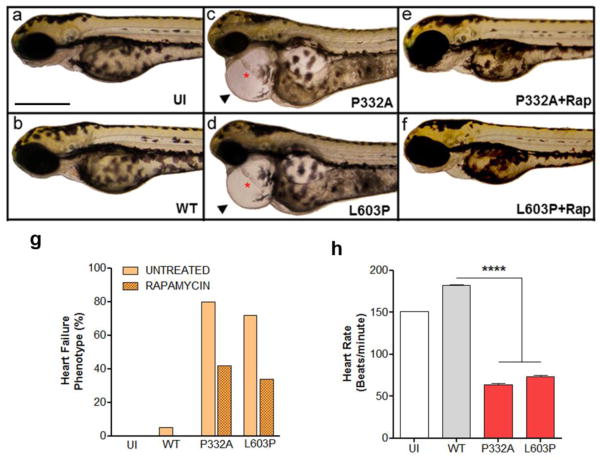
Figure 3. Dilated cardiomyopathy-associated RAF1 mutants induce heart defects mimicking heart failure phenotype in zebrafish.
Lateral view of zebrafish embryos at 72 hours post fertilization (hpf) that were uninjected (a), injected with WT (b), p.Pro332Ala (c) or p. Leu603Pro (d) RAF1 mRNA. The two representative dilated cardiomyopathy mutants (p.Pro332Ala and p.Leu603Pro) showing string-like cardiac chambers (asterisk) with pericardial edema (arrow). Treatment with rapamycin rescued the heart failure phenotypes in the p.Pro332Ala and p.Leu603Pro RAF1 mRNA-injected embryos (e and f, respectively). Scale bar, 500 μm. g. Percentage of zebrafish embryos at 72 hpf after injection of the indicated RAF1 mRNA exhibiting heart defects with and without rapamycin treatment (n=150 in each group). h. Measurements of mutant heart rate showing severe bradycardia at 72 hpf. Data represent means ± SD of 30 embryos. Reprinted with permission from Nature Genetics [38].