Figure 2.
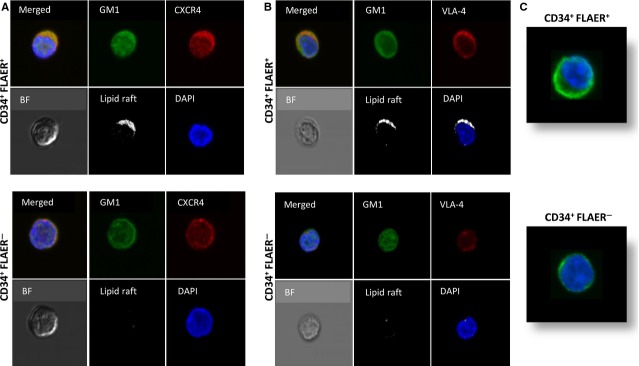
Defective adhesiveness and lipid raft formation in BM-derived CD34+ FLAER− cells (A and B). Representative images of CD34+ FLAER+ (normal) and CD34+ FLAER− (PNH) cells sorted from BM, stimulated by LL-37 (2.5 μg/ml), stained with cholera toxin subunit B (a lipid raft marker) conjugated with FITC, rabbit anti-hCXCR4 antibody with anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 594, rat antimouse VLA-4 with Alexa Fluor 594, and evaluated by confocal microscopy for formation of membrane lipid rafts. White areas indicate colocalization of CXCR4 (A) and VLA-4 (B) in membrane lipid rafts. It can be seen that lipid rafts were formed in CD34+ FLAER+ (normal), but not in CD34+ FLAER− (PNH) cells. The experiment was repeated with cells from three different patients, with similar results. (C). When plated in polylysine-coated dishes, CD34+ FLAER− cells, in contrast to normal healthy CD34+ FLAER+ cells, display a defect in actin polymerization. The experiment was repeated three times employing cells from different patients, with similar results.
