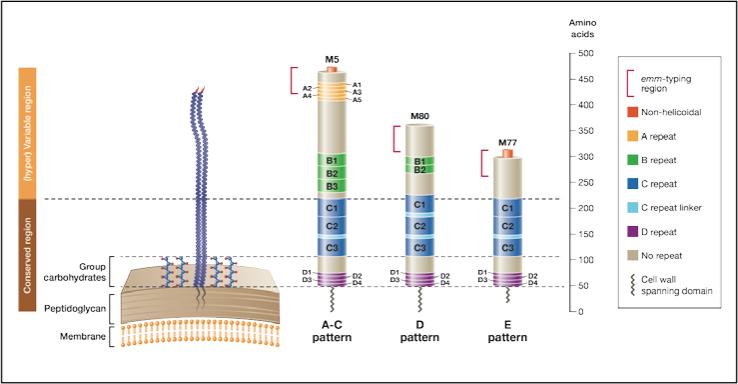
Figure 2. Three representative M proteins model.
Three representative M proteins (M5, M80 and M77) were selected as prototypes for the structural characteristics within each emm pattern group. M protein length and the size of the repeat and non-repeat regions are drawn to scale. Pattern A-C emm-types represent the longest M proteins, with a (hyper)variable portion of about 230 residues. In comparison, pattern D and E proteins possess a (hyper)variable portion of ~ 150 and 100 residues, respectively. The ‘A’ repeats are absent from the vast majority of M proteins belonging to the pattern D and E groups. The ‘B’ repeats are present in most of the pattern A-C and D emm-types, but absent from most of the pattern E emm-types. Thirty-five conserved residues constitute the ‘C’ repeat unit. Consecutive ‘C’ repeat units are sometimes separated by a seven residue unit called ‘C’ repeat linker (See supplementary data S2). Twenty percent of the M proteins (such as M80) do not possess non-helicoidal amino terminus. This proportion is 10%, 19% and 25% amongst the pattern A-C, D and E emm-types respectively. The portion of the protein considered by the emm-typing method is represented.