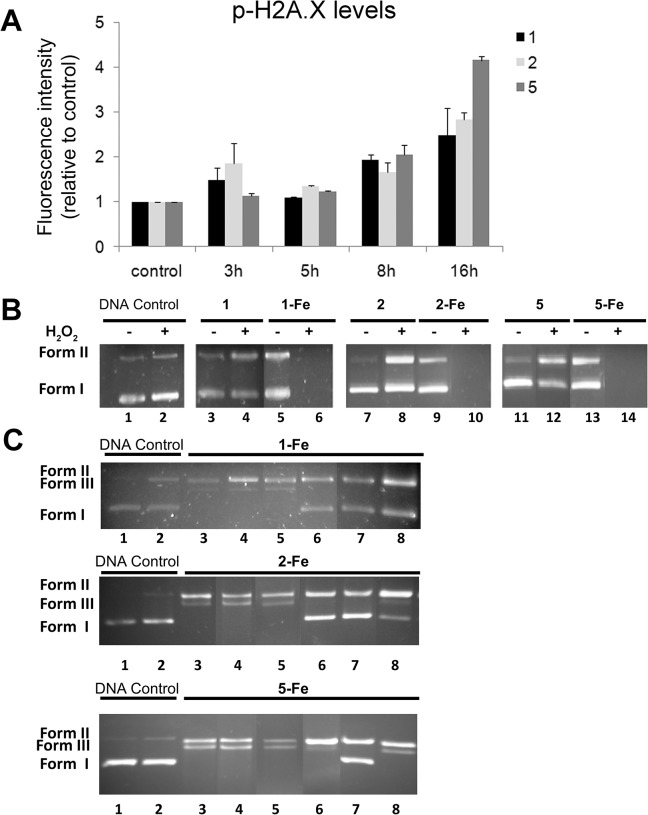
Fig 10. Analysis of the DNA damage induced by 1, 2 and 5.
(A) Quantification of cellular DNA damage. MCF-7 cells were exposed to 10 μmol/L 1, 2 and 5 for the indicated times and the levels of p-H2A.X were quantified using flow cytometry after immunostaining with anti-pH2A.X specific antibodies. The graph represents the mean fluorescence intensity for each experimental condition, relative to untreated cells. (B) Electrophoretic analysis of DNA cleavage. Supercoiled pUC18 plasmid DNA (18.9 μmol/L) was incubated with ligands 1, 2 and 5 and their respective Fe(II) complexes 1-Fe, 2-Fe and 5-Fe at 25 μM for 1 h (37°C). Lane 1, DNA control; lane 2, DNA control + H2O2; lane 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, ligand or Fe(II) complex in the absence of H2O2; lane 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, ligand or Fe(II) complex in the presence of H2O2. (C) Effect of groove binders and ROS scavengers on the cleavage of supercoiled pUC18 plasmid DNA treated with complexes 1-Fe, 2-Fe and 5-Fe at 15 μmol/L for 1 h (37°C) in the presence of H2O2. Lane 1, DNA control; lane 2, DNA control + H2O2; lane 3, complex control in the absence of potential inhibitors; lane 4, Hoechst 40 μmol/L; lane 5, methyl green 20 μmol/L; lane 6, Tiron 10 mmol/L; lane 7, sodium azide 0.4 mol/L; lane 8, 3 μL of DMSO.