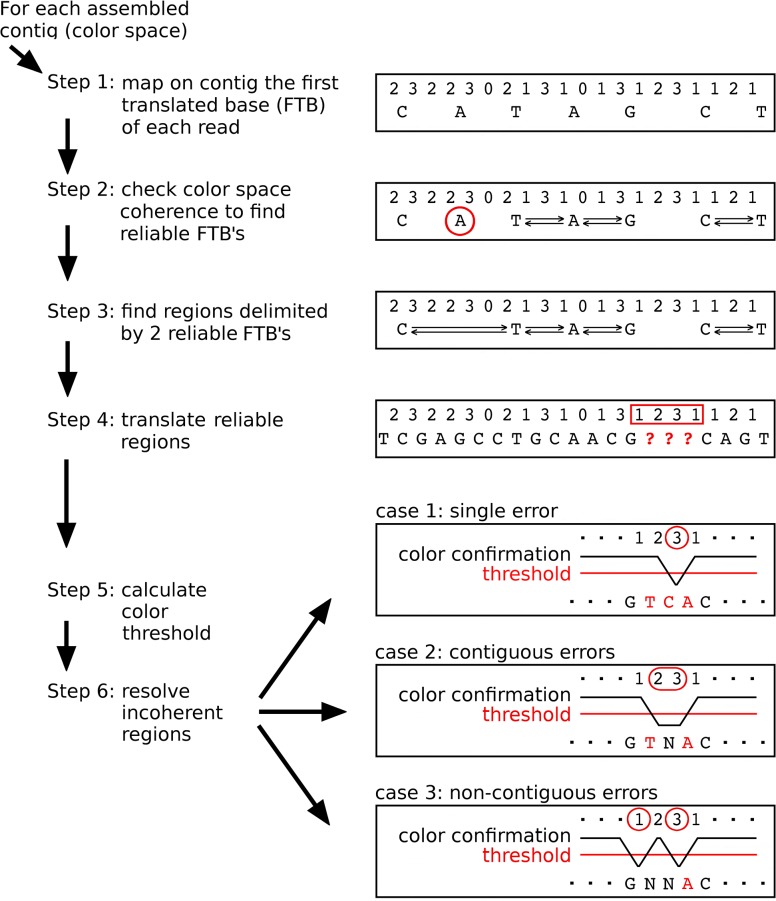
Fig 1. Flowchart of the color-translation process.
Step1: the first base (FTB) of each read can be translated from color-space with high accuracy; for each read the FTB is mapped on the contig. Step 2: check color coherence with neighboring FTBs; three conditions can be detected: a) FTBs coherent with their neighboring FTBs on both sides (such as the 'A' at the centre of the figure); FTB coherent only on one side (such as the 'G' that is coherent with the 'A', but not with the 'C'); FTBs with no coherence on both sides (such as the 'A' circled in red). The latter are removed from the assembly. Step 3 and 4: find regions delimited by two reliable start sites and translate color-space into base-space. Any remaining regions will be incoherent in terms of color compatibility. To resolve these regions the threshold for color reliability is calculated (Step 5) and the resulting value is used to establish the critical regions of the contig (Step 6).