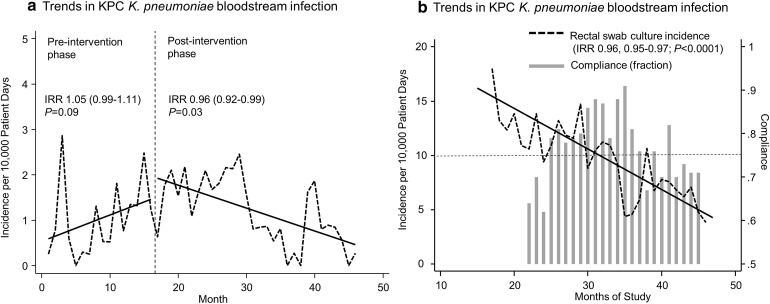
Fig. 1.
Monthly incidence trends in KPC-carbapenemase producing K. pneumoniae bloodstream infections (a) and colonization (b) detected by rectal swab cultures following introduction of a comprehensive antimicrobial stewardship and infection control program to limit carbapenem resistance. Dotted lines represent the monthly incidence per 10,000 patient days. Solid lines represent the incidence trends. Bars in panel b indicate monthly compliance rates of the fraction of patients who were appropriately screened with rectal cultures for KPC-carbapenemase producing K. pneumoniae. IRR calculated by segmented Poisson regression. Despite declining CRE rates, the IRRs of ESBL-positive Enterobacteriaceae were stable during the study period (IRR 1.02, 95% CI 0.99–1.04; P = 0.06). Likewise, we did not observe marked changes in the rates of MDR among MDR non-fermenting GNB (IRR 1.04, 95% CI 0.22–1.22, P = 0.132) or vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (IRR 0.98, 0.92–1.04; P = 0.57). IRR Incidence rate ratio, KPC K. pneumoniae carbapenemases