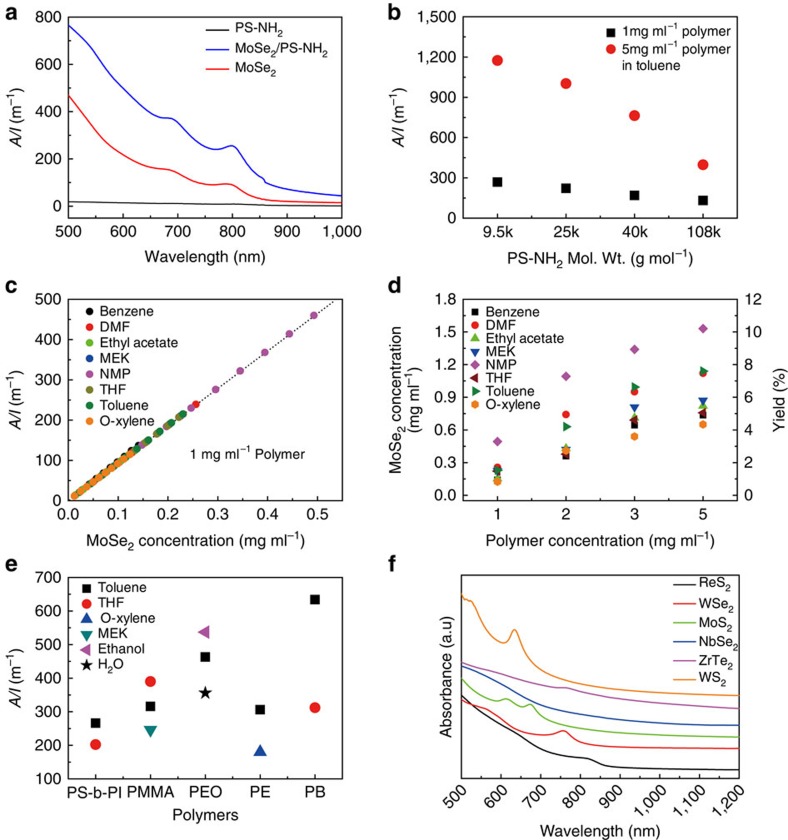
Figure 2. Dispersion characteristics of TMD nanosheets in organic solvents.
(a) Absorbance spectra of PS-NH2 (black), MoSe2 dispersed with PS-NH2 in toluene (blue) and MoSe2 dispersed without PS-NH2 in NMP (red). (b) Effect of the molecular weight of PS-NH2 on the efficiency of the MoSe2 dispersion in toluene characterized by the absorbance values of the dispersions at 800 nm. The initial concentrations of MoSe2 and PS-NH2 were kept constant at 10 mg ml−1 and 1 mg ml−1, respectively, for all of the molecular weights of PS-NH2 evaluated. Increasing the molecular weight of PS-NH2 leads to a decrease of the efficiency of the MoSe2 dispersion. (c) Absorbance at a wavelength of 800 nm as a function of the MoSe2 concentration in each solvent. The absorbance linearly increased with the amount of MoSe2 following Lambert–Beer behaviour, which implies uniform dispersion of MoSe2 without aggregation in all of the solvents. (d) Plots of the concentration of MoSe2 as a function of the initial concentration of PS-NH2 in different organic solvents. Yield of one to three layers (70%) of the exfoliated MoSe2 nanosheets with PS-NH2 as a function of the initial concentration of PS-NH2 in different organic solvents are also shown. (e) Absorbance per cell length (proportional to the concentration of dispersed MoSe2) of MoSe2 dispersed in a range of solvents with a concentration of 3 mg ml−1 of the different amine-terminated polymers. Note that PE-NH2 was dissolved in hot toluene and xylene. For MoSe2 dispersion in water with PEO-NH2, sonication was applied for 2 h. (f) Absorbance spectra of the dispersions of different TMDs exfoliated in toluene with PS-NH2. The absorbance spectra are vertically displaced for clarity.