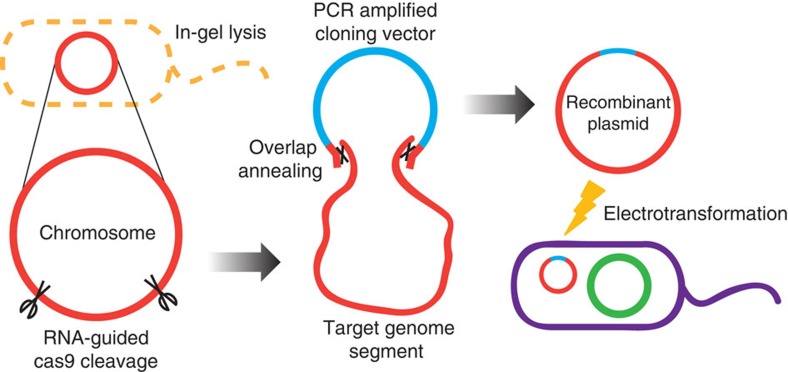
Figure 1. One-step large-gene-cluster cloning by CATCH.
After in-gel lysis of bacterial cells, the chromosomes are cleaved by RNA-guided Cas9 at the designated target sites. A cloning vector (length not to scale) that shares 30-bp terminal sequence overlaps (black cross) with the target DNA at both ends is ligated to the target segment in a Gibson assembly mix. The recombinant plasmid is then electrotransformed into a cloning host.