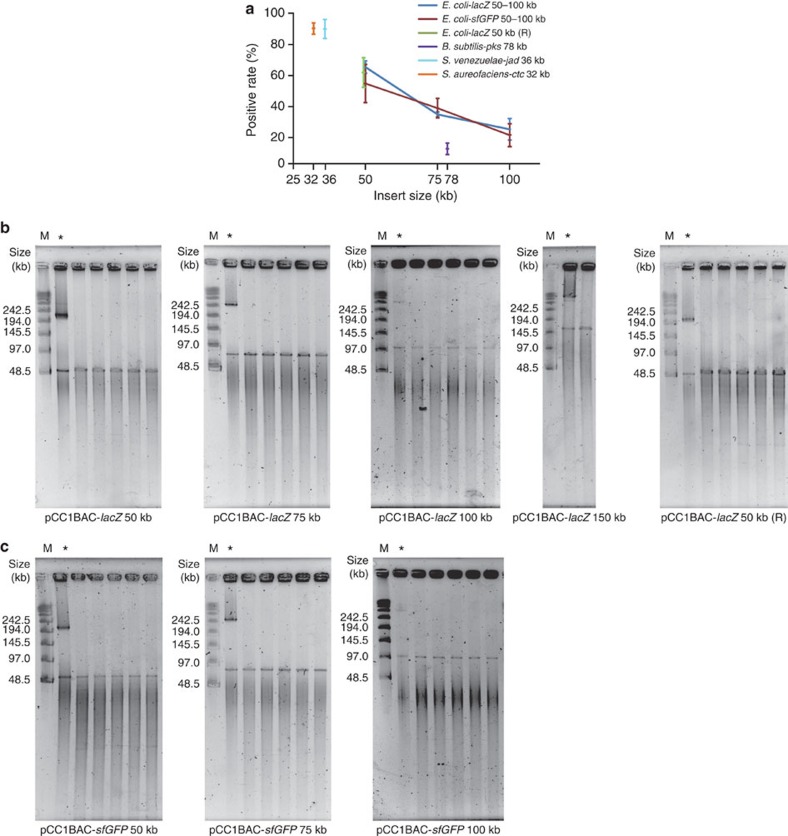
Figure 4. Efficiency of CATCH cloning of different genomic sequences.
(a) The positive rates of CATCH cloning with different insert sizes and target sequences from different genome locations, as well as from different bacteria are analysed (error bar: s.d.; n=3). E. coli-lacZ 50 kb (R) is the cloning result of a 50-kb genome segment targeted by lacZ-sgRNAs 7 and 8, with the PAM sequences falling on the flanking sequences instead of the target genome segment. (b) Plasmids carrying the target sequences of different lengths cloned from E. coli str. K-12 substr. MG1655 (ligated to an 8-kb BAC vector) were purified from the blue–white-screening- and PCR-positive clones, linearized and analysed by PFGE. (c) Plasmids carrying the target sequences of different lengths cloned from E. coli DH5a str. WPN25-sfGFP were purified, linearized and analysed by PFGE. M, marker; asterisk, λ-terminase-free control.