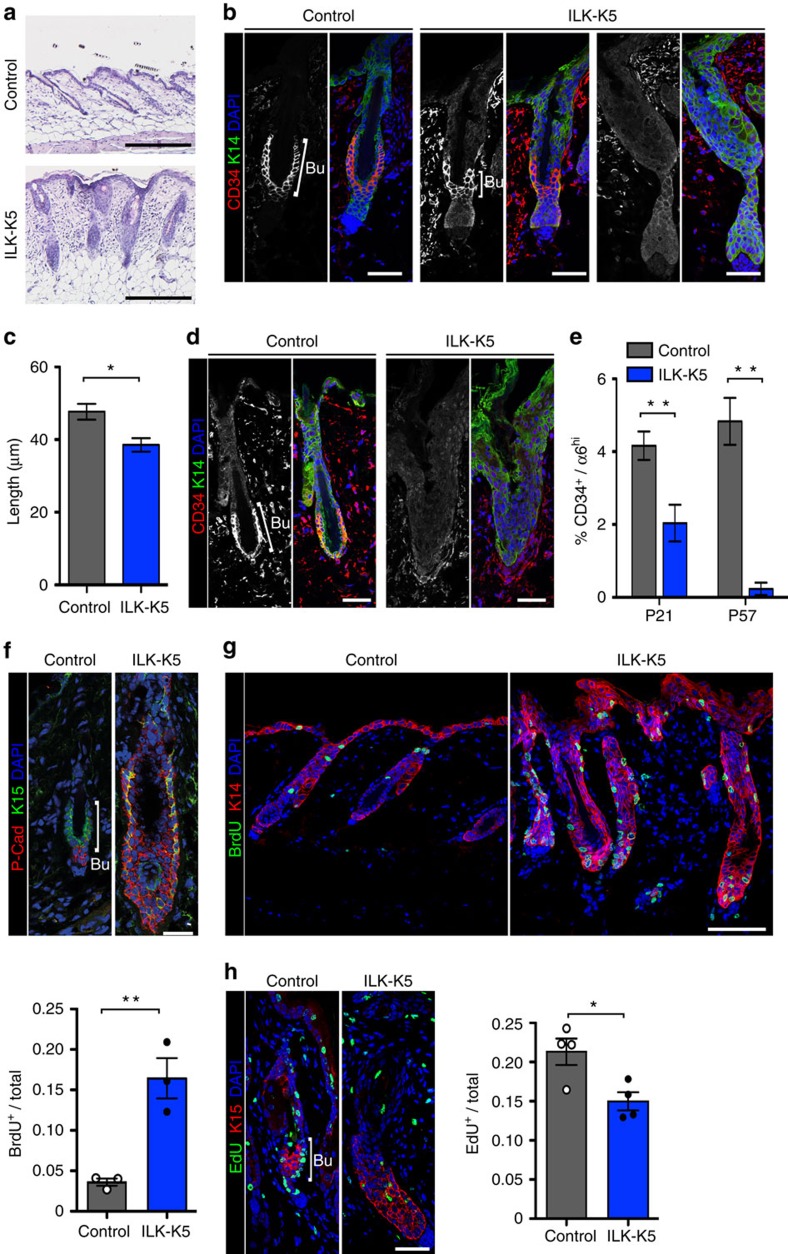
Figure 1. Deletion of ILK leads to progressive loss of quiescent bulge SCs.
(a) Haematoxylin/eosin staining of P21 skin. Compared with control HFs that display typical telogen morphology, ILK-K5 HFs are thick and more elongated, extending to the subcutis. Scale bar, 200 μm. (b) Immunofluorescence staining for the bulge SC marker CD34 (red) and EPC marker K14 (green) from P21 skin. CD34 staining within the bulge (Bu) is decreased or absent (right panel) in ILK-K5 HFs. Scale bars, 30 μm. (c) Quantification of bulge length from CD34 stainings at P21. Only HFs where CD34 staining was clearly present were measured (mean±s.e.m.; n=3; *P=0.05, Mann–Whitney). (d) CD34 staining from P57 skin shows absence of CD34-positive bulge SCs in ILK-K5 HFs. Scale bars, 30 μm. (e) FACS analysis of CD34+/α6 integrinhi bulge SCs shows progressive reduction of these cells in ILK-K5 skin (mean±s.e.m.; n=8; **P=0.0042 for P21; n=5; **P=0.0079 for P57; Mann–Whitney). (f) Immunofluorescence analysis of the HF progenitor marker K15 (green) and the TAC marker P-Cadherin (P-Cad; red) in P21 HFs shows expansion of both markers and mixing of the K15 and P-cad-positive compartments. Scale bars, 30 μm. (g) Detection of BrdU-positive cells within HFs of P21 mice after a 1 h BrdU pulse shows increased levels of BrdU-positive cells in ILK-K5 HFs. Scale bars, 50 μm. Values in quantification represent mean±s.e.m. of BrdU-positive cells per total HF cells (n=3; **P=0.0036, Mann–Whitney). (h) Analysis of EdU-positive LRCs within HFs of P21 mice after 10 days of EdU chase. Immunostaining shows decreased presence of LRCs in ILK-K5 bulge (Bu) SCs. Scale bars, 30 μm. Values in quantification represent mean±s.e.m. of EdU-positive cells per total cells in HFs (n=4; *P=0.05, Mann–Whitney). DAPI, 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.