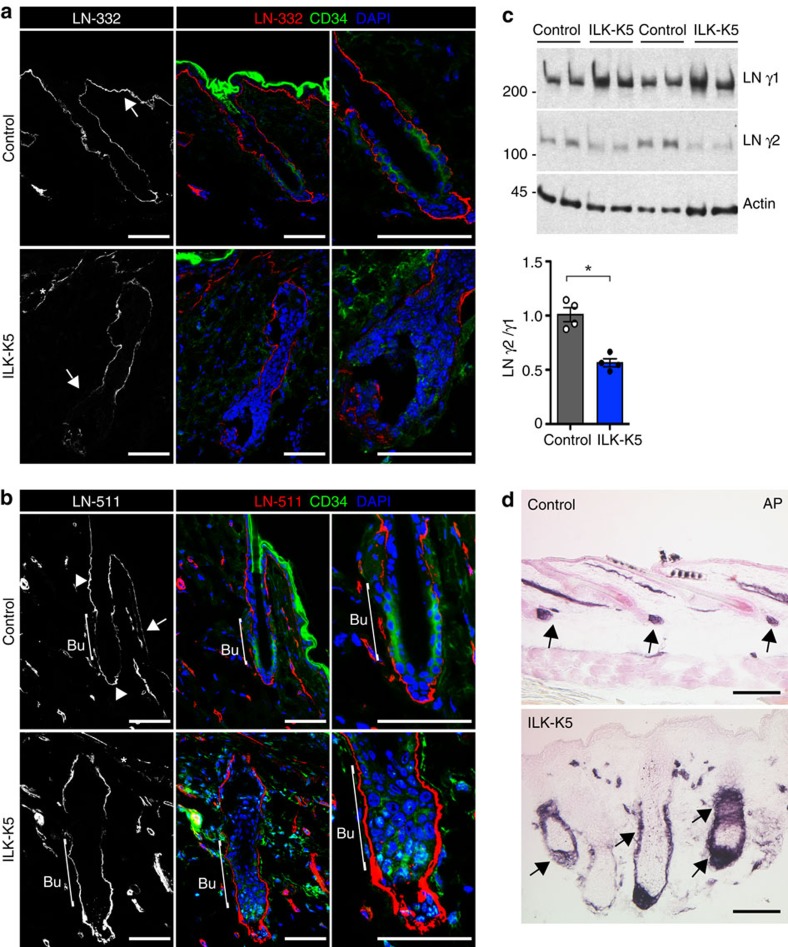
Figure 4. ILK is required to remodel the ECM around the bulge SC niche.
(a) Immunofluorescence staining for LN-332 (red) and CD34 (green) from P21 HFs. LN-332 staining shows higher intensity beneath IFE (arrow) than around HFs in control skin (upper panel). Note fragmentation of LN-332 staining along the IFE (asterisk) and decreased LN-332 around the lower part of the HF, including the HG (arrow) in ILK-K5 skin (lower panel). Scale bars, 50 μm. (b) Immunofluorescence staining for LN-511 (red) and CD34 (green) from P21 HFs. LN-511 staining shows highest intensity at the isthmus region and around HG (arrowheads). Only faint staining is observed beneath the IFE (arrow) and around bulge (bracket) in control skin (upper panel). Note fragmentation of LN-511 staining along the IFE (asterisk) and high intensity around bulge and HG (bracket) in ILK-K5 skin (lower panel). Scale bars, 50 μm. (c) Western blot analysis of LN γ1 and γ2 chains in skin extracts. Actin is used as a loading control. ILK-K5 skin shows increased levels of γ1 and decreased levels of γ2, resulting in a twofold decrease in γ2 to γ1 ratio. Lower panel shows quantifications of mean band intensities (mean±s.d.; n=4; *P=0.0286, Mann–Whitney). For full scans of western blots, see Supplementary Fig. 7. (d) Alkaline phosphatase (AP) staining to detect dermal papilla (DP) cells in P21 skin. In control skin, the DP is found attached to the base of each HF (arrows; upper panel). In ILK-K5 skin AP-positive cell population is increased and surrounds the entire lower region of the HFs (arrows; lower panel). Scale bars, 200 μm. DAPI, 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.