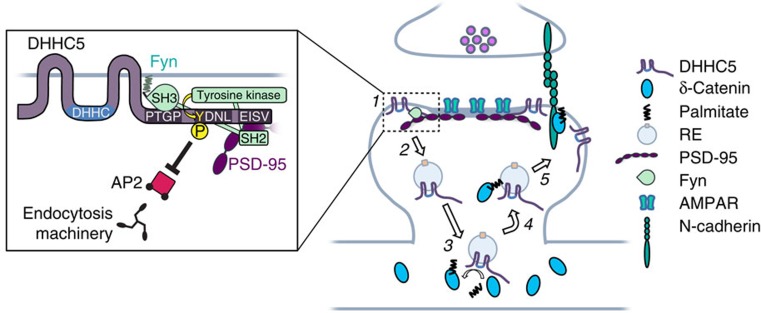
Figure 10. Model of activity-regulated trafficking of DHHC5.
(1 and inset) Under basal conditions, DHHC5 is localized to the postsynaptic membrane in complex with PSD-95 and Fyn. PSD-95 binds DHHC5 through PDZ-dependent mechanisms. Fyn binds to the C-terminal poly-proline motif (PTGP) of DHHC5 through its SH3 domain and phosphorylates DHHC5 Y533 within the DHHC5 endocytic motif (YDNL). This inhibits the binding of the endocytic adaptor protein, AP2, to DHHC5. (2) Increased neuronal activity enhances STEP61-mediated dephosphorylation of Fyn and reduces its kinase activity (not shown), as well as decreases DHHC5 association with PSD-95 and Fyn, thereby enhancing DHHC5 internalization and trafficking to dendritic shafts on REs (2–3 min post stimulation). (3) DHHC5 associates with δ-catenin and palmitoylates it (3–10 min post stimulation). (4) DHHC5 and palmitoylated δ-catenin traffic back into spines (3–20 min post stimulation). (5) DHHC5 dissociates from δ-catenin and is reinserted into the synaptic membrane (10–20 min post stimulation). Significantly more DHHC5 is recruited to the synaptic membrane 20 min post stimulation compared with basal levels. δ-Catenin binds and stabilizes N-cadherin, leading to enhancements in synapse structure and increased membrane stabilization of AMPARs 20–60 min post stimulation. The association of δ-catenin with PSD-95 and Fyn, and δ-catenin tyrosine phosphorylation are also increased 20 min post stimulation (not shown), possibly linking cadherin–adhesion complexes with receptor-scaffold assemblies to coordinate synapse strengthening.