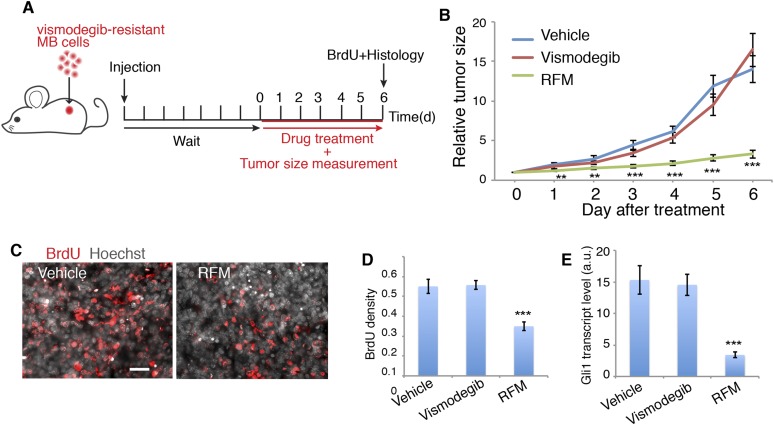
Figure 7. PDE4 inhibitors suppress Hh signal transduction and Hh-related tumor growth.
(A) Schematic diagram of the MB tumor allograft experiment in mouse. Drug treatment started 6 day after injection when the size of tumors could be accurately measured. (B) The relative tumor size is defined as the tumor volume on the indicated day divided by that on day 0. For each drug 9–10 mice were used. (C, D) BrdU density in tumors after drug treatment. Scale: 50 μm. (E) Hh signal transduction in tumors was assessed by Gli1 transcription level through qPCR. RFM: roflumilast. Error bars represent SEM. Statistics: Student's t-Test. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.