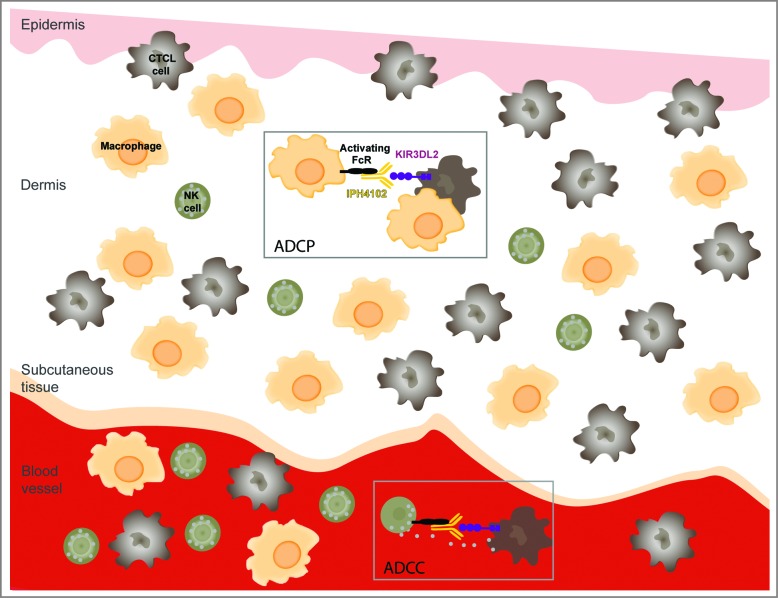
Figure 1.
Potential immune antitumor modes of action of IPH4102 in CTCL. Binding of IPH4102 to Fc receptor-bearing natural killer (NK) cells or macrophages leads to the targeting and elimination of KIR3DL2+ cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) tumor cells by antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity (ADCC) or/and antibody-dependent cell phagocytosis (ADCP). Because of the reciprocal relative ratios of NK cells to macrophages in the blood stream and skin, one can predominantly expect ADCC in the blood and ADCP in the dermis as immunologic mechanisms of tumor target elimination.