Figure 3. Ghrelin attenuates glucose-induced [Ca2+]i increases in β-cells in a GHSR-dependent manner.
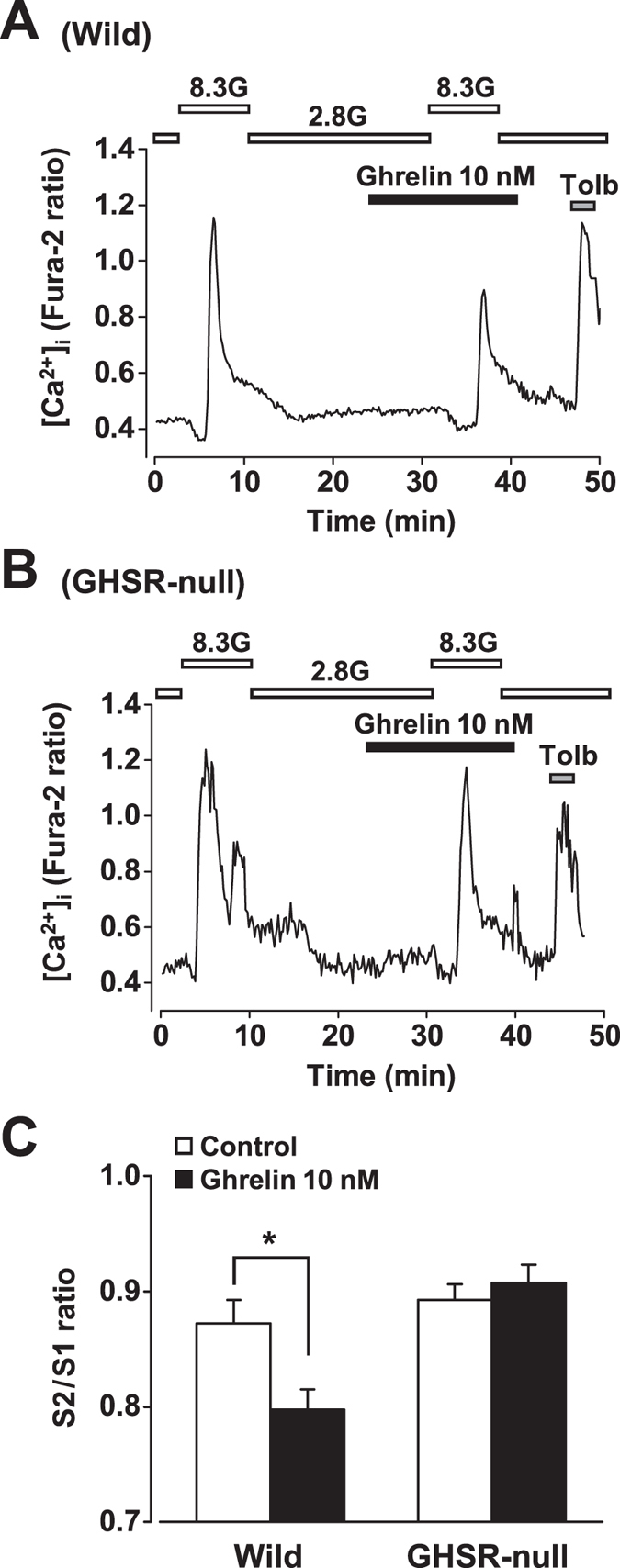
(A) Glucose (8.3 mM) increased [Ca2+]i in β-cells isolated from islets of wild-type mice. The glucose (8.3 mM)-induced [Ca2+]i increase was suppressed by ghrelin (10 nM), which was added to superfusion solution 5 min prior to the second glucose stimulation. (B) Ghrelin failed to suppress glucose (8.3 mM)-induced [Ca2+]i increases in β-cells from GHSR-null mice. (C) The ratio of the peak amplitude of [Ca2+]i increases in responses to the second glucose (8.3 mM) stimulation (S2) over that to the first glucose stimulation (S1), S2/S1, was decreased by ghrelin (10 nM), indicating inhibition of [Ca2+]i responses. The ability of ghrelin to suppress glucose (8.3 mM)-induced [Ca2+]i increases was abolished in GHSR-null β-cells (n = 74–150 cells). *P < 0.05.
