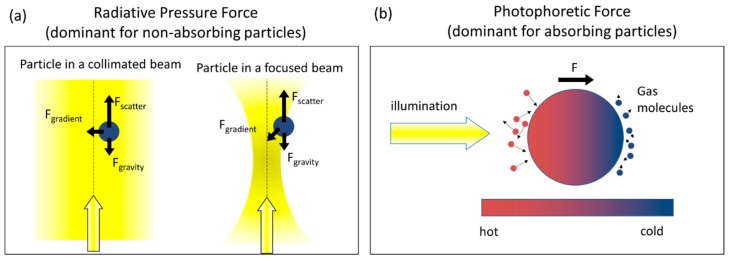
Figure 1.
(a) The radiative pressure force, which is the dominant force experienced by non-absorbing particles, results from the transfer of momentum from photons scattered by a particle. The radiative pressure force can be divided into a scattering force, which tends to push the particle along the direction of light propagation, and a gradient force, which tends to pull the particle toward the highest intensity region. The gradient force enables trapping in a focused laser beam; (b) The photophoretic force, which is the dominant force experienced by strongly absorbing particles, results from the transfer of heat to surrounding gas molecules from a non-uniformly heated and/or non-uniformly heat-emitting particle.