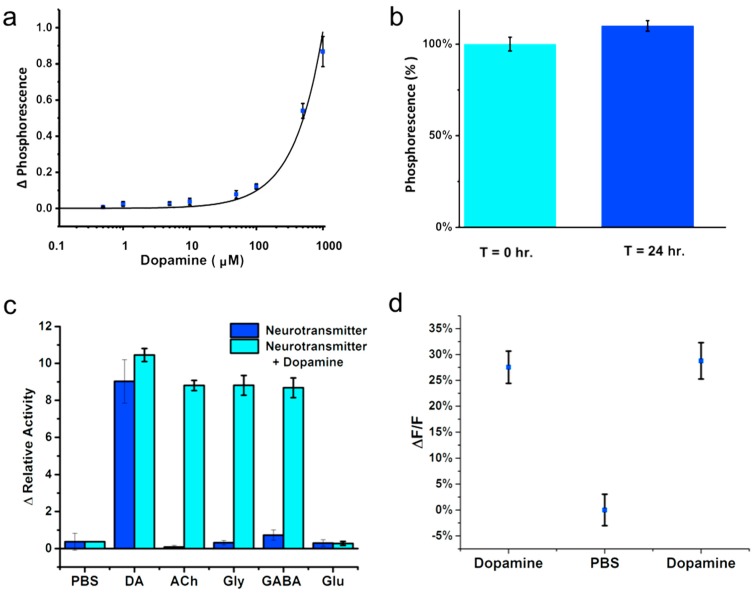
Figure 4.
The nanosensors’ sensitivity and selectivity were measured using phosphorescence spectroscopy. (a) Response of dopamine sensing nanosensors from 0.01 μM–1·mM dopamine with a limit of detection of 110 μM (Δ Phosphorescence rate); (b) The nanosensors showed minimal dye leaching in solution and were stable over 24 h of consecutive phosphorescence measurements; (c) The selectivity of the nanosensors was examined by exposing the nanosensors to 10 mM neurotransmitter solutions of GABA, L-glutamate (Glu), glycine (Gly), and acetylcholine (ACh). Subsequent additions of 10 mM dopamine were added to confirm recovery of nanosensors activity. The neurotransmitters did not display changes in activity; except L-glutamate inhibited tyrosinase as expected; (d) The QuID phosphorescent response and recovery to cycles of 1 mM dopamine and PBS pH 7.4.