Figure 5.
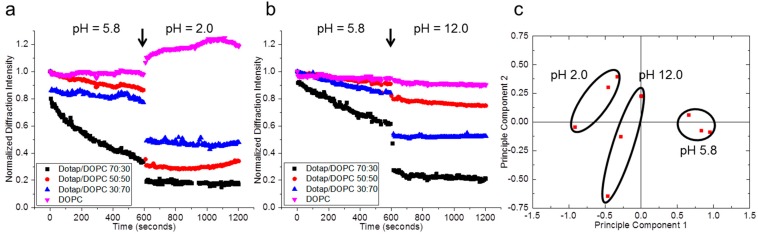
Detection of pH changes under water. Principal component analysis (PCA) results in separated clusters of lipid grating responses to different pH. (a,b) Normalized diffraction intensity of lipid multilayer gratings consisting of different charge. Upon immersion into deionized water of pH 5.8, the lipid gratings undergo different degrees of spreading to account for decreases in diffraction signal. Upon altering the pH after 10 min of incubation to either more acidic Figure 5a or basic Figure 5b conditions, changes in diffraction signal are realized after allowing adjusted solution to incubate for ten more minutes; (c) Clustering in principal component space suggests the lipid multilayer grating array chip can distinguish acidic and basic conditions. The first two principal components account for 86.46% of the total variance in the set of pH experiments.