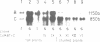Abstract
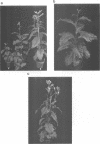
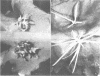
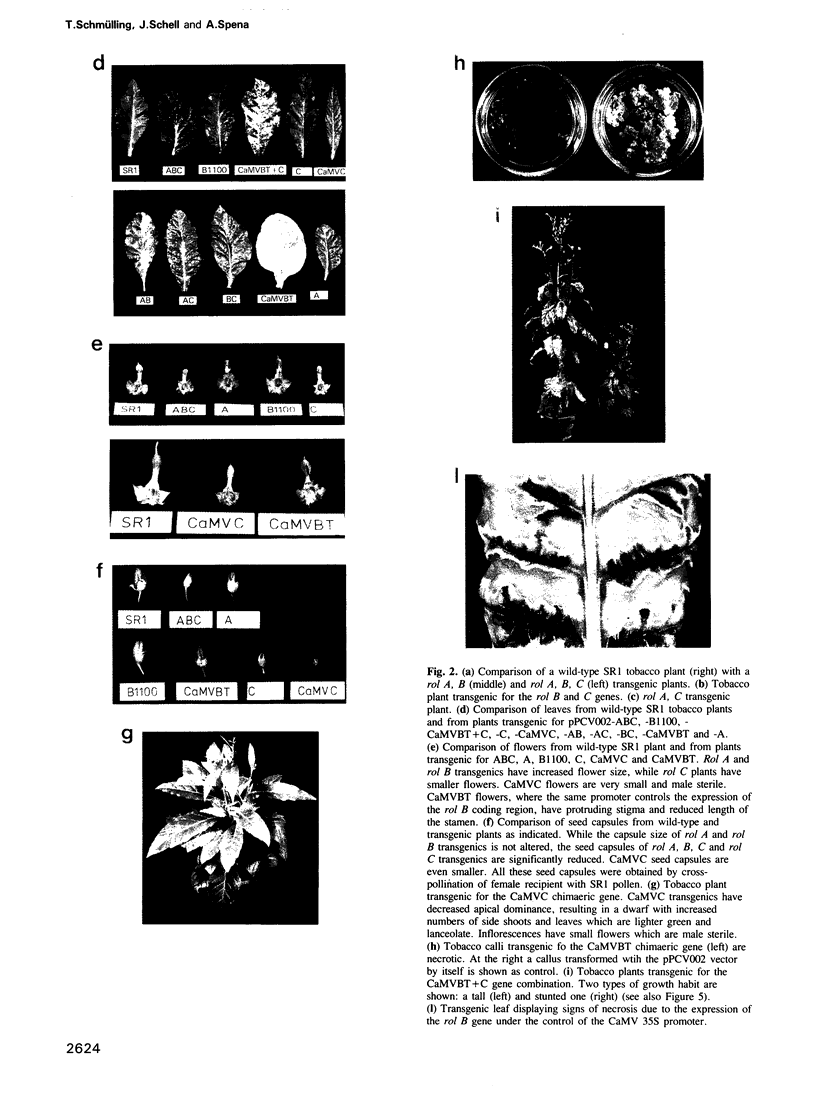
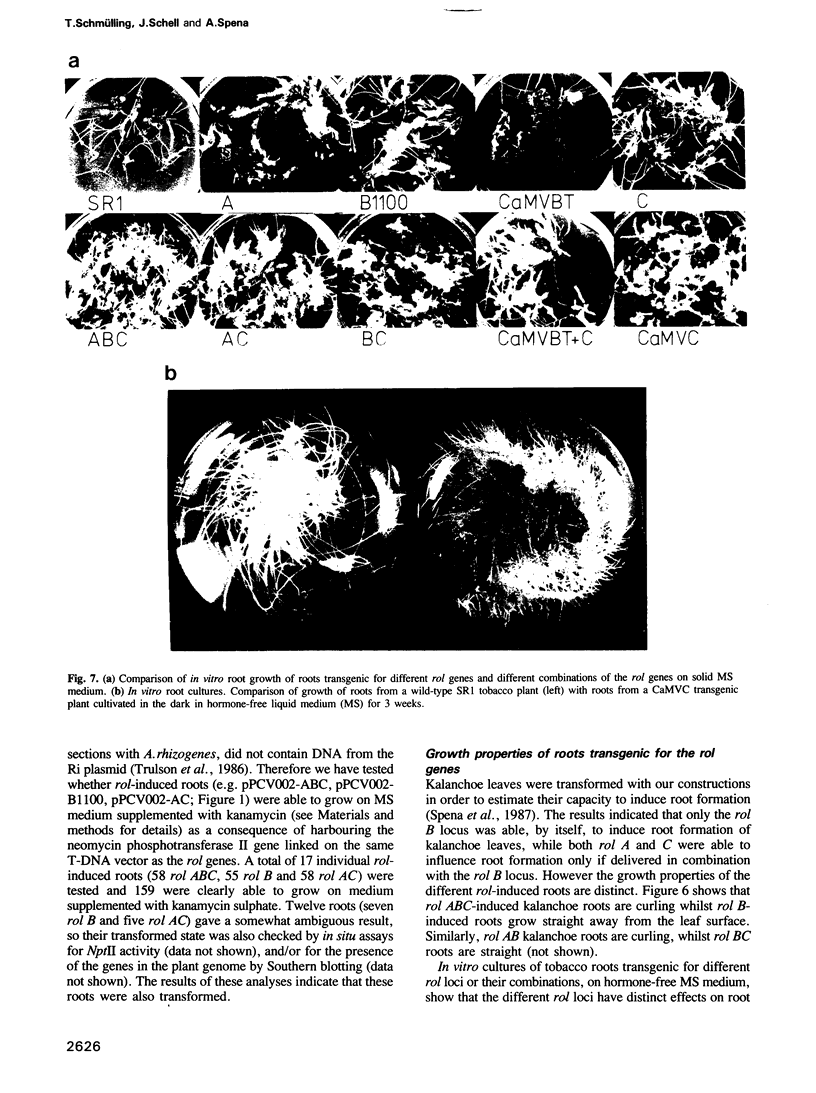
The combined expression of the rol A, B and C loci of Agrobacterium rhizogens Ri-plasmids establishes, in transgenic tobacco plants, a pathological state called hairy-root syndrome. However, when expressed separately they provoke distinct developmental abnormalities characteristic for each rol gene. Moreover, changes in their mode of expression obtained by replacing the promoters of the rol B and C genes with the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter elicit new and distinct developmental patterns. These results indicate that the different rol gene products have either different targets, or have a qualitatively different effect on the same target. The target(s) must be involved in the control of plant development. Although each of the three rol genes are independently able to promote root formation in tobacco, efficient root initiation and growth is best achieved through the combined activities of more than a single rol gene. Models explaining the biological effects of A. rhizogenes-derived TL-DNA genes are discussed.
Keywords: developmental genes, Agrobacterium rhizogenes, transgenic plants, male sterility
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyoshi D. E., Klee H., Amasino R. M., Nester E. W., Gordon M. P. T-DNA of Agrobacterium tumefaciens encodes an enzyme of cytokinin biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5994–5998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry G. F., Rogers S. G., Fraley R. T., Brand L. Identification of a cloned cytokinin biosynthetic gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4776–4780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmann I., Marner F. J., Schröder G., Waffenschmidt S., Schröder J. Tumour genes in plants: T-DNA encoded cytokinin biosynthesis. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):853–859. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03710.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardarelli M, Mariotti D, Pomponi M, Spanò L, Capone I, Costantino P. Agrobacterium rhizogenes T-DNA genes capable of inducing hairy root phenotype. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Oct;209(3):475–480. doi: 10.1007/BF00331152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comai L., Kosuge T. Involvement of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid in indoleacetic acid synthesis in Pseudomonas savastanoi. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):950–957. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.950-957.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand-Tardif M., Broglie R., Slightom J., Tepfer D. Structure and expression of Ri T-DNA from Agrobacterium rhizogenes in Nicotiana tabacum. Organ and phenotypic specificity. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 5;186(3):557–564. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90130-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsch R. B., Fraley R. T., Rogers S. G., Sanders P. R., Lloyd A., Hoffmann N. Inheritance of functional foreign genes in plants. Science. 1984 Feb 3;223(4635):496–498. doi: 10.1126/science.223.4635.496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson R. A., Kavanagh T. A., Bevan M. W. GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3901–3907. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02730.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murai N., Skoog F., Doyle M. E., Hanson R. S. Relationships between cytokinin production, presence of plasmids, and fasciation caused by strains of Corynebacterium fascians. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):619–623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell J. T., Nagy F., Chua N. H. Identification of DNA sequences required for activity of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):810–812. doi: 10.1038/313810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder G., Waffenschmidt S., Weiler E. W., Schröder J. The T-region of Ti plasmids codes for an enzyme synthesizing indole-3-acetic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 16;138(2):387–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07927.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slightom J. L., Durand-Tardif M., Jouanin L., Tepfer D. Nucleotide sequence analysis of TL-DNA of Agrobacterium rhizogenes agropine type plasmid. Identification of open reading frames. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):108–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spena A., Hain R., Ziervogel U., Saedler H., Schell J. Construction of a heat-inducible gene for plants. Demonstration of heat-inducible activity of the Drosophila hsp70 promoter in plants. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2739–2743. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03997.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spena A., Schmülling T., Koncz C., Schell J. S. Independent and synergistic activity of rol A, B and C loci in stimulating abnormal growth in plants. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3891–3899. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02729.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tepfer D. Transformation of several species of higher plants by Agrobacterium rhizogenes: sexual transmission of the transformed genotype and phenotype. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):959–967. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90430-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow L. S., Reeves S., Thomashow M. F. Crown gall oncogenesis: evidence that a T-DNA gene from the Agrobacterium Ti plasmid pTiA6 encodes an enzyme that catalyzes synthesis of indoleacetic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5071–5075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White F. F., Taylor B. H., Huffman G. A., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Molecular and genetic analysis of the transferred DNA regions of the root-inducing plasmid of Agrobacterium rhizogenes. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):33–44. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.33-44.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Palm C. J., Brooks B., Kosuge T. Nucleotide sequences of the Pseudomonas savastanoi indoleacetic acid genes show homology with Agrobacterium tumefaciens T-DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6522–6526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]