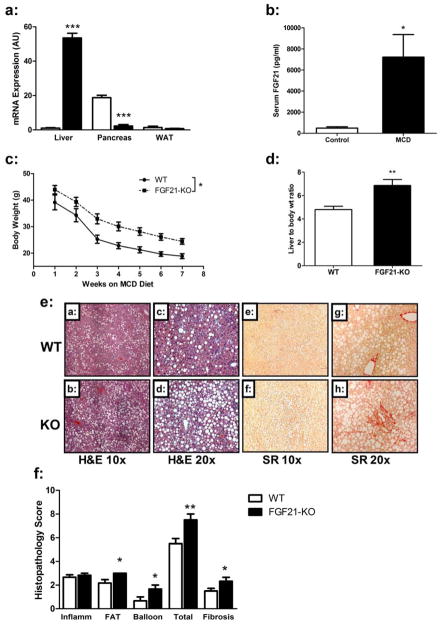
Figure 1. FGF21 is up regulated in a mouse model of steatohepatitis a condition which is severely exacerbated in Fgf21-deficient mice.
(a) Fgf21 mRNA expression is markedly increased in livers of WT mice on the MCD diet for 2 weeks, decreased in the pancreas, and unchanged in white adipose tissue. (b) Fgf21 serum levels are elevated in WT mice on the MCD diet for 2 weeks. (c) When consuming an MCD diet for the duration of 8 weeks mice lacking FGF21 (FGF21-KO) remain heavier than WT littermates after 8 weeks on the MCD diet. (d) FGF21-KO mice have increased liver to body weight ratio. Histological analysis of steatohepatitis in FGF21KO mice. (e) FGF21-KO mice have increased lipid accumulation compared to WT mice (panels a–d, stained by H&E, at 10x and 20x magnification), and increased perisinusoidal, perivenular, and periportal fibrosis as assessed by Sirius Red (SR) staining (panels e–h, at 20x and 40x magnification). (f) Histopathology scores assigned to the FGF21-KO livers showed higher scores for fatty change (FAT), hepatocyte ballooning (BALLOON), total NAFLD Activity Score (TOTAL), and fibrosis. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, N = 6 per group. (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01).