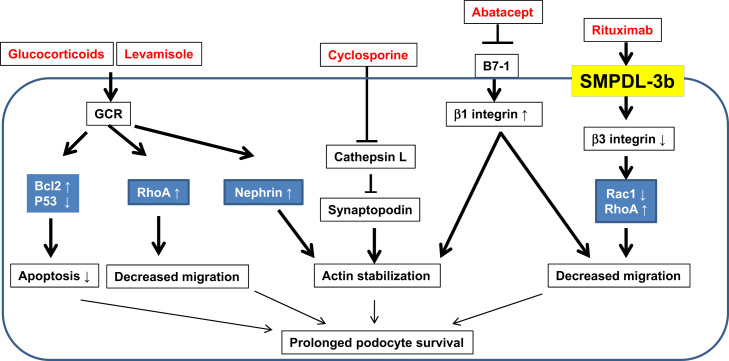
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram showing nonimmunologic targets of immunosuppressive agents in podocytes. Glucocorticoids and levamisole attenuate podocyte apoptosis and increase in RhoA activity and decrease in degradation of synaptopodin protein. Soluble urokinase receptor and lipopolysaccharide activate B7-1 signaling and cathepsin L activity, whereas cyclosporine and abatacept inhibit synaptopodin degradation. Rituximab enhances sphingomyelinase-like phosphodiesterase 3b expression and stabilizes synaptopodin.
GCR, glucocorticoids receptor; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; SMPDL-3b; sphingomyelinase-like phosphodiesterase 3b; suPAR, soluble urokinase receptor.