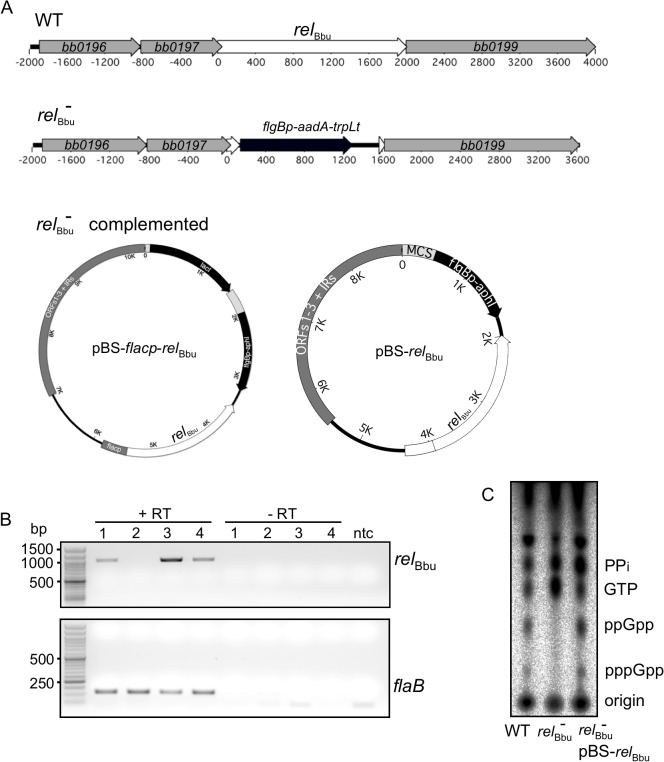
Fig 3. Mutation and complementation of rel Bbu in B. burgdorferi.
(A) The rel Bbu mutant (rel Bbu -) was constructed by replacing the rel Bbu gene in strain B31-5A4 with the streptomycin resistance gene aadA fused to the B. burgdorferi flgB promoter and the B. subtilis trpL terminator. The rel Bbu mutant was complemented in trans by transformation with the Borrelia shuttle vector pBSV2 containing the rel Bbu gene fused to either the flacp inducible promoter (pBS-flacp-rel Bbu) or its native promoter (pBS-rel Bbu). (B) RT-PCR analysis of RNA isolated from wild-type (lane 1), rel Bbu - (lane 2), rel Bbu - pBS-flacp-rel Bbu (lane 3), or rel Bbu - pBS-rel Bbu (lane 4) strains. Samples were incubated with (+RT) or without (-RT) reverse transcriptase, and rel Bbu and flaB transcripts were detected by PCR using primer pairs rsh 981F/rsh 1984R and flaB 423F/flaB 542R, respectively. Products were separated on 1% (rel Bbu) or 2% (flaB) agarose gels and stained with ethidium bromide. ntc = no template control. (C) Production of (p)ppGpp in the wild-type (WT), rel Bbu - and rel Bbu - pBS-rel Bbu (rel Bbu - comp) strains. 32P-labeled cultures were grown to log phase, shifted to RPMI for 6 h and nucleotides were extracted and analyzed by TLC.