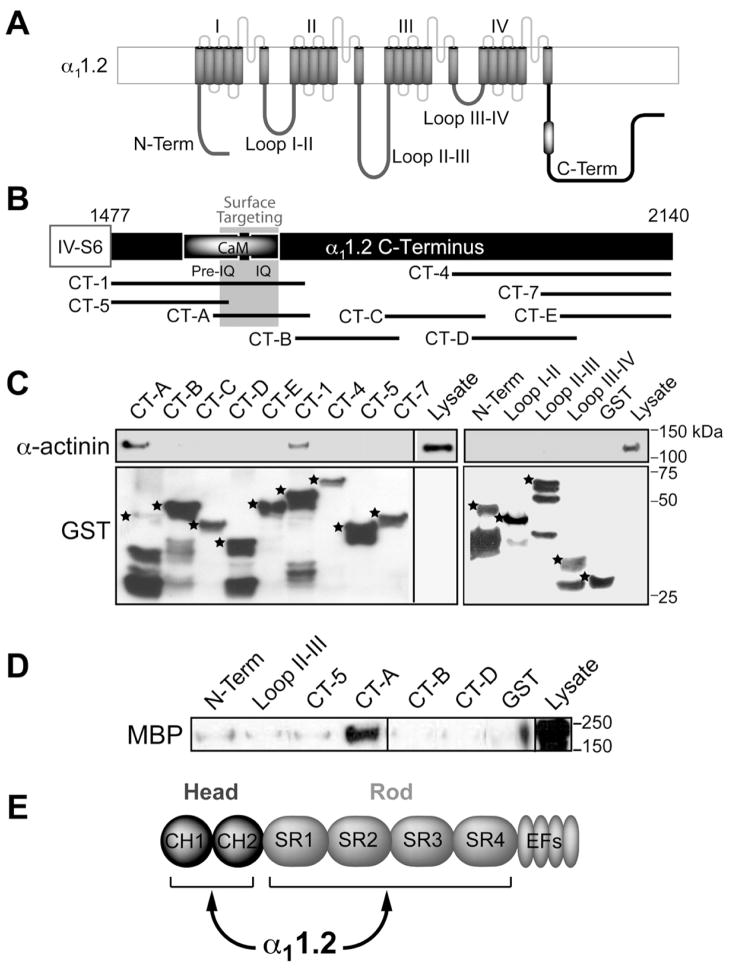
Figure 2. α-Actinin-1 Interacts with the CaM Binding and Surface Targeting Region of the α11.2 C-terminus.
(A) Diagram of α11.2 depicts intracellular N- and C-termini and four homologous domains, which form the channel pore and are connected by intracellular loops. Black and white oval: Pre-IQ + IQ region.
(B) Diagram of the α11.2 C-terminus depicts the Pre-IQ + IQ CaM binding region, the surface targeting region (residues 1626–1666 (Gao et al., 2000)), and the overlapping C-terminal GST fusion proteins used.
(C) IB of α-actinin pull-down from rat forebrain homogenates by indicated GST fusion proteins. Top, probing for α-actinin binding to GST fusion proteins. α-actinin bound to CT-1 [corresponding to rabbit α11.2 residues 1507–1733 (NFDYL…GGLFG)] and to CT-A [corresponding to rat α11.2 residues 1584–1707 (ELRAI…FGNHV); the latter are homologous to rabbit residues 1614–1737; the change in numbering is because the rat sequence lacks 30 residues at the very N-terminus compared to rabbit]. Bottom, probing for total GST fusion protein present within each pull-down reaction. While there are comparable amounts of expected full length forms for most fusion proteins (*), the C-terminal half of CT-A is largely removed identifying the N-terminal half as α-actinin binding site. In addition, the 20 residues at the N-terminus, which would overlap with the C-terminal 20 residues of CT-A, (SAASEDDIFRRAGGLFGNHV) do not apparently bind α-actinin.
(D) IB of pull-down of purified MBP-α-actinin-1 by immobilized α11.2 GST fusion proteins using an anti-MBP antibody. CT-A directly interacts with α-actinin.
(E) Schematic illustrates head and rod domain of α-actinin.
See also Table S1 for details on subcloning.