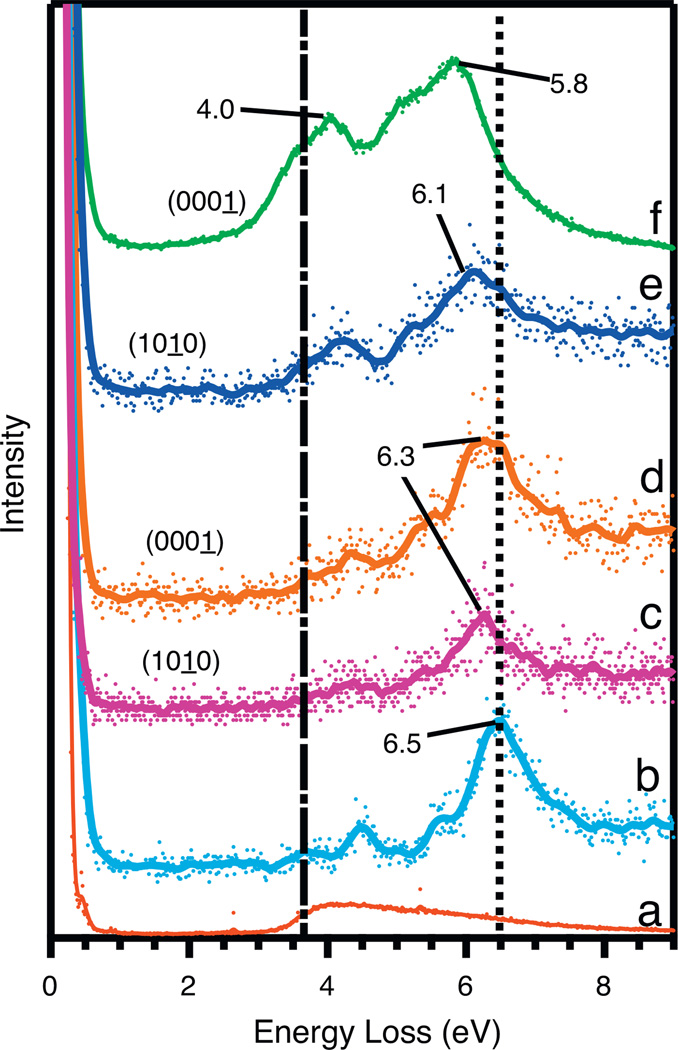
Figure 2.
EELS spectra of 100 L phenol adsorbed to the (1 0 1̱ 0) and the (0 0 0 1̱)-Zn surfaces at various temperatures. The spectra are as follows: (a) clean (0 0 0 1̱)-Zn: (b) adsorption at −177 °C on (1 0 1̱ 0); (c) adsorption on (1 0 1̱ 0) at room temperature; (d) adsorption on (0 0 0 1̱)-Zn at room temperature; (e) adsorption on (1 0 1̱ 0) at 220 °C; and (f) adsorption on (0 0 0 1̱)-Zn at 220 °C. The dotted vertical line is aligned to the 6.5 eV loss peak of the thick physisorbed phenol layer at −177 °C. The dot-dash vertical line on the left is aligned with the midpoint of the ZnO band gap at approximately 3.6 eV (a). All spectra are normalized to the elastic peak.