Fig. 1.
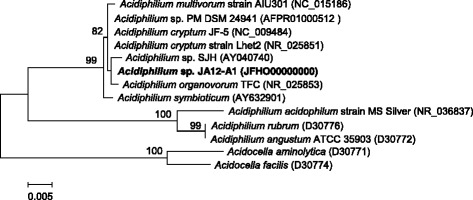
Dendrogram of strains of the genus Acidiphilium - based on partial 16S rRNA gene sequences. The dendrogram was calculated with MEGA5 [20] using the Maximum Likelihood method based on the Jukes-Cantor model [21]. The analyzed sequences were aligned by CLUSTALW [22]. The clustering of the sequences was tested by the bootstrap approach with 1000 repeats. The length of the tree branches was scaled according to the number of substitutions per site (see size bar). All strains used in the analysis, except Acidiphilium cryptum JF-5 and Acidiphilium sp. SJH, are type strains of their respective species [23–30] with Acidiphilium cryptum representing the genus Acidiphilium as the designated type species [2]. Acidocella aminolytica (D300771) and Acidocella facilis (D30774) were used as outgroup. The 16S rRNA gene sequence for Acidiphilium sp. PM DSM 24941 can be found under the locus tag APM_R0045 on contig Ctg_00688 (AFPR01000512) of the whole genome shotgun sequence. Whole genome sequences are only available for Acidiphilium cryptum JF-5, Acidiphilium multivorum AIU301, Acidiphilium sp. PM DSM 24941 and Acidiphilium angustum ATCC 35903 (GOLD project IDs: Gc00559, Gc01862, Gi09776, Gi0051610; accession numbers: NC_009484, NC_015186; AFPR00000000, JNJH00000000)
