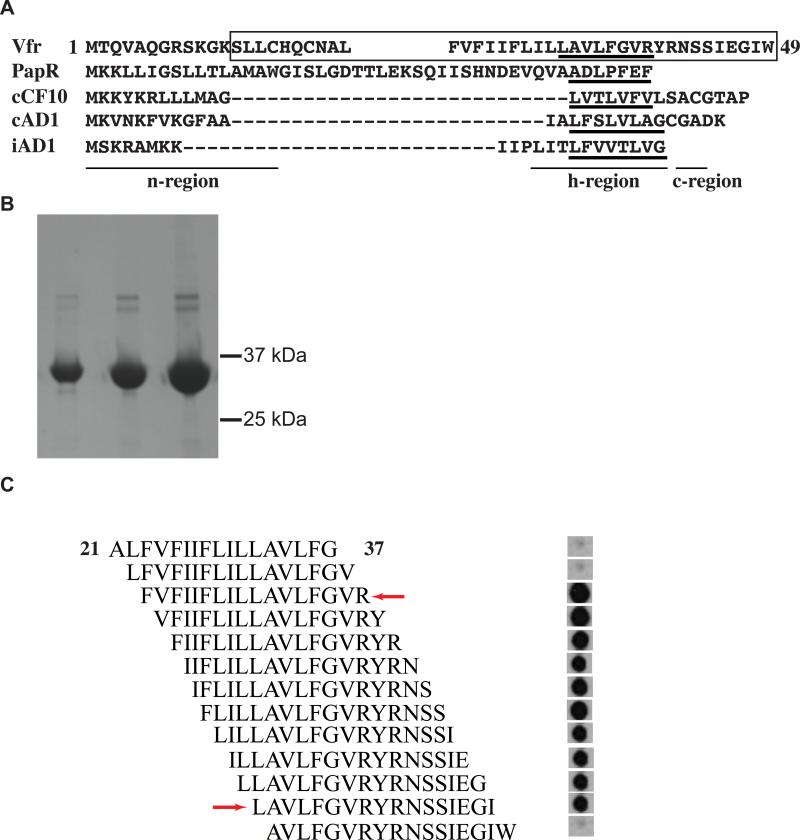
Figure 5. Recombinant RopB binds the Vfr amino-terminus signal sequence.
(A) Primary sequence alignment of Vfr signal sequence with characterized Gram-positive bacterial pheromones, PapR from Bacillus cereus; and cCF10, cAD1, and iAD1 from Enterococcus faecalis. Regions corresponding to the three major components of signaling peptides, n-region, h-region, and c-region, are underlined and labeled. Amino acid sequences corresponding to mature peptides of each pheromone and the putative Vfr mature peptide were underlined. Amino acid sequences of Vfr included in the peptide array are boxed. (B) SDS-polyacrylamide gel with increasing concentrations of purified recombinant hexa-histidine tagged RopB. The corresponding positions of molecular weight markers (in kilodaltons) are indicated. (C) Peptide array of overlapping 17-mer peptides that spans the entire putative Vfr signal sequence was generated using SPOT synthesis on a cellulose membrane. Membrane was incubated with purified recombinant hexa-histidine tagged RopB, and bound protein was detected with anti-hexahistidine tag antibodies and chemiluminescence. The red arrows indicate the likely amino-terminal and carboxy-terminal boundaries of the RopB binding site in the Vfr secretion signal sequence, located at L32 and R39 amino acid residues, respectively. The numbering of amino acid residues indicates their position within the Vfr secretion signal sequence.