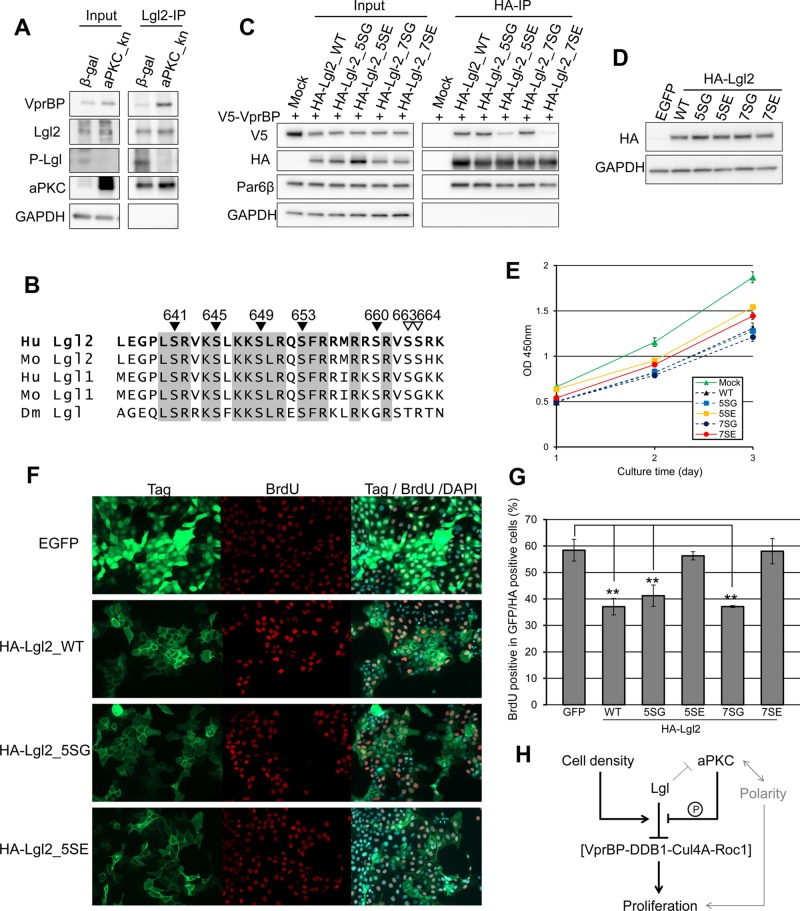
FIGURE 6:
Phosphorylation of Lgl2 impairs the interaction between Lgl2 and VprBP, and phosphomimetic mutations attenuate the proliferation-suppressive function of Lgl2. (A) MDCK cells were infected by adenovirus vector expressing LacZ or dominant-negative PKCλ (K273E). Then Lgl2 was immunoprecipitated from cell lysates. Note that the expression of the kinase-negative aPKC suppressed phosphorylation of Lgl2 and enhanced the interaction between Lgl2 and VprBP. (B) Alignment of amino acid sequences around aPKC-mediated phosphorylation sites of Lgl1 or 2 of human, mouse, and fly. The numbers show the amino acid sequence of human Lgl2. Closed inverted triangles show mutated residues in 5S mutants, and open inverted triangles show additional residues mutated in 7S mutants. (C) V5-VprBP and HA-Lgl2 or its mutants were overexpressed in HEK293T cells. Then HA-Lgl2 and its mutants were immunoprecipitated using anti-HA antibody. Note that phosphomimetic mutants of Lgl2 showed low affinity for VprBP. (D) Episomally stable transformants were obtained by selection with G418 after introduction of pEB vector encoding Lgl2 and its mutants, and equal expression was confirmed among these transformants. Immunoblot was performed using whole-cell lysates of 48 h–cultured cells after reseeding. (E) WST-8 cell proliferation assay using episomally stable MDCK transformants expressing Lgl2 and its mutants. Error bars indicate ±SD. (F) Episomally stable MDCK cells expressing Lgl2 and its mutants were reseeded sparsely and cultured for 2 d. Then the BrdU incorporation assay was performed. Note that not all cells expressed transgene. Cells with introduced pEB vector encoding enhanced GFP were used as a control. (G) The ratio of BrdU-positive cells to total cells in the experiment in F was determined, and averages of three independent experiments are plotted. Error bars indicate ±SD. Double asterisk denotes significant difference (p < 0.01) by Student's t test. (H) Schematic representation of Lgl-mediated proliferation inhibition. Lgl inhibits formation of the CRL4 [VprBP] complex, and this inhibition is controlled by aPKC-mediated phosphorylation, cell density, or yet-unknown mechanism. Cell polarity regulation may also affect regulation of proliferation.