A novel calcium benzoate complex, [Ca(C7H5O2)2(C2H6OS)], has been synthesized and structurally characterized. The compound has a chain polymeric structure stabilized by C—H⋯π interactions.
Keywords: crystal structure, calcium benzoate, coordination polymer, C—H⋯π interactions
Abstract
In the title complex, [Ca(C7H5O2)2(C2H6OS)]n, the Ca2+ ion (site symmetry m..) is surrounded by eight O atoms, six from two bridging–chelating tridentate benzoate carboxyl groups and two from a bridging dimethyl sulfoxide molecule (point group symmetry m..), giving an irregular coordination geometry [Ca—O bond length range = 2.345 (2)–2.524 (2) Å]. One-dimensional coordination complex chains extending parallel to c are generated in which the triply μ2-O-bridged Ca2+ cations are separated by 3.6401 (5) Å. In the crystal, weak intrachain C—H⋯π hydrogen bonds are present between the methyl H atoms of the dimethyl sulfoxide molecules as donors and the aromatic rings as acceptors [C—H⋯Cg = 3.790 (4) Å].
Chemical context
Compounds of benzoic acid with calcium are of special interest due to their wide-ranging applications, for example as a preservative in the food industry, in cosmetics and in medicine. In spite of that, the crystal structures of such compounds have been poorly investigated. Searches of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD; Version 5.35, November 2013 + 2 updates; Groom & Allen, 2014 ▸) for simple calcium benzoate complexes revealed only three results: [Ca(benz)2(dmf)(H2O)]n (Yano et al., 2001 ▸), {[Ca(benz)(H2O)3]+ (benz)−}n (Senkovska & Thewalt, 2005 ▸) and [Ca(benz)2(Hbenz)(H2O)]n (Azizov et al., 2011 ▸) (where benz = benzoate). 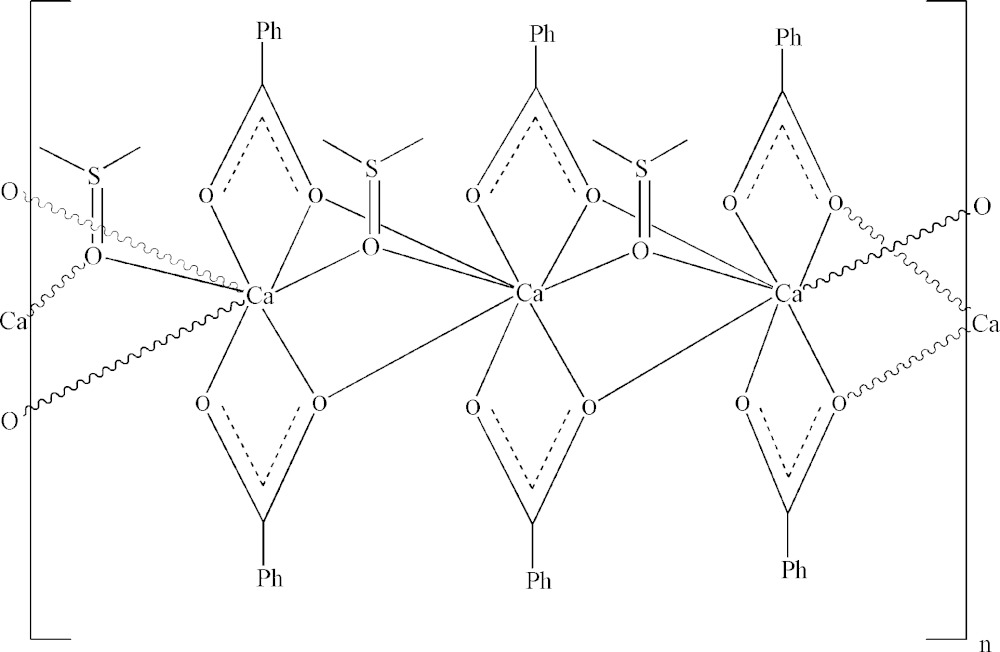
Here we report the synthesis of a new calcium benzoate–dimethyl sulfoxide complex, [Ca(benz)2(dmso)]n, which was obtained as a by-product of an attempted synthesis of an Mn/Cu heterometallic complex (in crystalline form available for X-ray analysis) from the system: Mn–Cu–(bhz–sal)–CaO–KSCN–dmso (in open air), where manganese and copper were used as unactivated metal powders, bhz = benzohydrazide and sal = salicylaldehyde. The investigation of the system was carried out as a part of systematic research on the elaboration the ‘direct synthesis’ approach to both homo- and heterometallic coordination compounds (Babich et al., 1996 ▸; Buvaylo et al., 2005 ▸; Vassilyeva et al., 1997 ▸). It is worth noting that an alternative method of synthesis using a classical reaction between calcium oxide and benzoic acid in dmso, affords the same complex in good yield (up to 90%), but does not give X-ray quality crystals. The crystal structure of the title complex, [Ca(benz)2(dmso)]n, is reported herein.
Structural commentary
The asymmetric unit of [Ca(benz)2(dmso)]n comprises one Ca2+ cation (site symmetry m..), one benzoate ligand and half of a dmso molecule, the other half being generated by mirror symetry. The irregular CaO8 coordination polyhedron consists of six O atom donors from two O,O′ chelating-bridging benzoate carboxyl groups with the same coordination modes, [2.11112] in the Harris notation (Coxall et al., 2000 ▸), and two from μ2-bridging dmso molecules (Fig. 1 ▸). The coordination geometry deviates strongly from ideal, the Ca—O bond lengths varying from 2.345 (2) to 2.524 (2) Å (Table 1 ▸) and the O—Ca—O angles from 52.19 (7) to 156.06 (8)°. The bridging Ca1—O1i and Ca1—O1ii (carboxyl) bond lengths are considerably shorter than the chelate ones, as is usually observed in polymeric benzoates. For the title complex, the bond-valence index [BVS (Ca)] (Allmann, 1975 ▸) is 2.03.
Figure 1.
A fragment of the [Ca(benz)2(dmso)]n chain with the atom-labelling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms have been omitted for clarity. For symmetry codes, see Table 1 ▸.
Table 1. Selected bond lengths ().
| Ca1O1i | 2.345(2) | Ca1O3 | 2.494(3) |
| Ca1O1ii | 2.345(2) | Ca1O3iv | 2.516(3) |
| Ca1O2iii | 2.481(2) | Ca1O1iii | 2.524(2) |
| Ca1O2 | 2.481(2) | Ca1O1 | 2.524(2) |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  .
.
Supramolecular features
The triple-O-bridged CaO8 polyhedra form one-dimensional coordination polymeric chains which extend parallel to the c-axis direction (Figs. 2 ▸–4 ▸
▸). The Ca⋯Cai and Ca1⋯Ca1iv separation in the chain is 3.6401 (5) Å [symmetry code (iv): −x + 1, −y, z −  ]. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first Ca carboxylate polymer based on non-centrosymmetric bridges (μ-η2:η1)2. For bridging modes in coordination polymeric structures, reference should be made to Deacon et al. (2007 ▸) and Busskamp et al. (2007 ▸). The polymer chains in the title compound are additionally stabilized by weak C—H⋯π interactions between the methyl groups of the dmso molecule and the benzoate rings (centroid Cg) (Table 2 ▸, Figs. 3 ▸ and 4 ▸).
]. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first Ca carboxylate polymer based on non-centrosymmetric bridges (μ-η2:η1)2. For bridging modes in coordination polymeric structures, reference should be made to Deacon et al. (2007 ▸) and Busskamp et al. (2007 ▸). The polymer chains in the title compound are additionally stabilized by weak C—H⋯π interactions between the methyl groups of the dmso molecule and the benzoate rings (centroid Cg) (Table 2 ▸, Figs. 3 ▸ and 4 ▸).
Figure 2.
Bridging interactions observed in the title complex polymer which extends along the c- axis direction. Phenyl rings and H atoms have been omitted for clarity.
Figure 3.
C—H⋯π hydrogen bonds involving a dmso donor as found in the title complex. For symmetry codes, see Table 1 ▸).
Figure 4.
Packing of the molecular chains viewed down the chain direction (the crystallographic c axis). C—H⋯π bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Table 2. CH interactions (, ).
Cg is the centroid of the benzoate ring.
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C8H8A Cg | 0.96 | 2.84 | 3.790(4) | 169 |
Synthesis and crystallization
Calcium oxide (0.056 g, 1 mmol) and benzoic acid (0.244 g, 2 mmol) were added to 20 ml of dmso and stirred magnetically for ca 5 h at 323 K, after which the solution was filtered. The white precipitate which formed after one day was collected and dried in air; yield: 0.4 g (90%). Elemental analysis for C16H16CaO5S (M r = 360.43). Calculated: Ca, 11.12%; found: Ca, 11.0%. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1603 (s), 1562 (s), 1405 (s), 1024 (s), 721 (s). Crystals suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained by slow evaporation at room temperature of a solution which was the product from the reaction between manganese powder (0.05 g, 1 mmol), copper powder (0.06 g, 1 mmol), benzohydrazide (0.409 g, 3 mmol), salicylaldehyde (0.314 ml, 3 mmol), CaO (0.168 g, 3 mmol), KSCN (0.291 g, 3 mmol) and dmso (20 ml). The reaction was carried out at 353 K with magnetic stirring for eight hours, after which undissolved products were filtered off.
Refinement details
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are given in Table 3 ▸. Hydrogen atoms were placed in calculated positions [C—Haromatic = 0.95; C—Hmethyl = 0.99 Å] and were allowed to ride in the refinements, with U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(aromatic C) or 1.5U eq(methyl C). Although not of relevance in this crystal involving achiral molecules, the Flack absolute structure parameter (Flack, 1983 ▸) was determined as 0.04 (8) by classical fit to all intensities and 0.07 (3) from 557 selected quotients (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸).
Table 3. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | [Ca(C7H5O2)2(C2H6OS)] |
| M r | 360.43 |
| Crystal system, space group | Orthorhombic, C m c21 |
| Temperature (K) | 200 |
| a, b, c () | 25.531(2), 9.5351(8), 6.9330(4) |
| V (3) | 1687.7(2) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo K |
| (mm1) | 0.52 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.22 0.15 0.11 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Rigaku Mercury CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (Blessing, 1995 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.798, 0.951 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2(I)] reflections | 3704, 1897, 1676 |
| R int | 0.025 |
| (sin /)max (1) | 0.683 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.044, 0.103, 1.13 |
| No. of reflections | 1897 |
| No. of parameters | 109 |
| No. of restraints | 1 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| max, min (e 3) | 0.59, 0.39 |
| Absolute structure | Flack x determined using 557 quotients [(I +)(I )]/[(I +)+(I )] (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸) |
| Absolute structure parameter | 0.07(3) |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015012487/zs2334sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015012487/zs2334Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 1409468
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
This work was partly supported by the State Fund for Fundamental Research of Ukraine (project 54.3/005).
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| [Ca(C7H5O2)2(C2H6OS)] | Dx = 1.418 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 360.43 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71069 Å |
| Orthorhombic, Cmc21 | Cell parameters from 1872 reflections |
| a = 25.531 (2) Å | θ = 2.3–28.7° |
| b = 9.5351 (8) Å | µ = 0.52 mm−1 |
| c = 6.9330 (4) Å | T = 200 K |
| V = 1687.7 (2) Å3 | Block, colorless |
| Z = 4 | 0.22 × 0.15 × 0.11 mm |
| F(000) = 752 |
Data collection
| Rigaku Mercury CCD (2x2 bin mode) diffractometer | 1897 independent reflections |
| Graphite monochromator | 1676 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 14.7059 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.025 |
| dtprofit.ref scans | θmax = 29.0°, θmin = 2.3° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (Blessing, 1995) | h = −34→26 |
| Tmin = 0.798, Tmax = 0.951 | k = −12→6 |
| 3704 measured reflections | l = −9→9 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.044 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.103 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.040P)2 + 0.7932P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.13 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 1897 reflections | Δρmax = 0.59 e Å−3 |
| 109 parameters | Δρmin = −0.39 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 557 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] (Parsons et al., 2013) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Absolute structure parameter: 0.07 (3) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Ca1 | 0.5000 | 0.05825 (7) | 0.36175 (11) | 0.0325 (2) | |
| O1 | 0.44205 (8) | 0.06089 (19) | 0.0668 (3) | 0.0388 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.43213 (9) | 0.2334 (2) | 0.2748 (4) | 0.0509 (6) | |
| O3 | 0.5000 | 0.1724 (3) | 0.6855 (5) | 0.0414 (7) | |
| C1 | 0.41769 (12) | 0.1682 (3) | 0.1275 (5) | 0.0375 (7) | |
| C2 | 0.37045 (12) | 0.2146 (3) | 0.0171 (5) | 0.0388 (7) | |
| C3 | 0.35274 (13) | 0.1367 (4) | −0.1381 (7) | 0.0589 (10) | |
| H3 | 0.3695 | 0.0533 | −0.1704 | 0.071* | |
| C4 | 0.31036 (16) | 0.1818 (5) | −0.2452 (8) | 0.0756 (13) | |
| H4 | 0.2988 | 0.1289 | −0.3495 | 0.091* | |
| C5 | 0.28529 (14) | 0.3044 (4) | −0.1984 (7) | 0.0624 (11) | |
| H5 | 0.2567 | 0.3340 | −0.2707 | 0.075* | |
| C6 | 0.30222 (15) | 0.3831 (4) | −0.0461 (7) | 0.0584 (11) | |
| H6 | 0.2855 | 0.4669 | −0.0160 | 0.070* | |
| C7 | 0.34453 (12) | 0.3375 (3) | 0.0639 (6) | 0.0464 (8) | |
| H7 | 0.3555 | 0.3900 | 0.1695 | 0.056* | |
| C8 | 0.44725 (16) | 0.4090 (3) | 0.6588 (6) | 0.0560 (10) | |
| H8A | 0.4146 | 0.3721 | 0.7051 | 0.084* | |
| H8B | 0.4493 | 0.3964 | 0.5217 | 0.084* | |
| H8C | 0.4494 | 0.5071 | 0.6889 | 0.084* | |
| S1 | 0.5000 | 0.31863 (10) | 0.77164 (16) | 0.0444 (3) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Ca1 | 0.0504 (4) | 0.0257 (3) | 0.0214 (4) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.0005 (3) |
| O1 | 0.0472 (11) | 0.0343 (11) | 0.0349 (13) | 0.0085 (8) | 0.0000 (10) | −0.0033 (9) |
| O2 | 0.0720 (14) | 0.0427 (12) | 0.0381 (13) | 0.0142 (11) | −0.0139 (13) | −0.0064 (11) |
| O3 | 0.069 (2) | 0.0218 (12) | 0.0333 (17) | 0.000 | 0.000 | −0.0020 (12) |
| C1 | 0.0515 (17) | 0.0302 (14) | 0.0307 (17) | 0.0017 (13) | 0.0019 (13) | 0.0022 (12) |
| C2 | 0.0421 (15) | 0.0389 (16) | 0.0353 (17) | 0.0002 (13) | 0.0011 (13) | 0.0042 (14) |
| C3 | 0.0556 (18) | 0.060 (2) | 0.061 (2) | 0.0180 (16) | −0.014 (2) | −0.022 (2) |
| C4 | 0.067 (2) | 0.086 (3) | 0.074 (3) | 0.020 (2) | −0.031 (2) | −0.022 (3) |
| C5 | 0.0483 (19) | 0.069 (2) | 0.070 (3) | 0.0101 (19) | −0.0107 (18) | 0.010 (2) |
| C6 | 0.0478 (19) | 0.045 (2) | 0.082 (3) | 0.0097 (16) | 0.0054 (19) | 0.003 (2) |
| C7 | 0.0483 (17) | 0.0390 (17) | 0.052 (2) | 0.0063 (14) | 0.0025 (16) | −0.0028 (16) |
| C8 | 0.083 (3) | 0.0357 (15) | 0.049 (2) | 0.0096 (17) | 0.005 (2) | −0.0010 (17) |
| S1 | 0.0829 (8) | 0.0257 (5) | 0.0244 (6) | 0.000 | 0.000 | −0.0015 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Ca1—O1i | 2.345 (2) | C1—C2 | 1.496 (4) |
| Ca1—O1ii | 2.345 (2) | C2—C3 | 1.383 (5) |
| Ca1—O2iii | 2.481 (2) | C2—C7 | 1.384 (4) |
| Ca1—O2 | 2.481 (2) | C3—C4 | 1.381 (5) |
| Ca1—O3 | 2.494 (3) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| Ca1—O3iv | 2.516 (3) | C4—C5 | 1.371 (5) |
| Ca1—O1iii | 2.524 (2) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| Ca1—O1 | 2.524 (2) | C5—C6 | 1.365 (6) |
| Ca1—C1iii | 2.855 (3) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| Ca1—C1 | 2.855 (3) | C6—C7 | 1.392 (5) |
| Ca1—Ca1i | 3.6401 (5) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| Ca1—Ca1iv | 3.6401 (5) | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| O1—C1 | 1.269 (3) | C8—S1 | 1.780 (4) |
| O1—Ca1iv | 2.345 (2) | C8—H8A | 0.9600 |
| O2—C1 | 1.251 (4) | C8—H8B | 0.9600 |
| O3—S1 | 1.517 (3) | C8—H8C | 0.9600 |
| O3—Ca1i | 2.516 (3) | S1—C8iii | 1.780 (4) |
| O1i—Ca1—O1ii | 78.22 (11) | C1iii—Ca1—Ca1i | 130.82 (7) |
| O1i—Ca1—O2iii | 91.88 (8) | C1—Ca1—Ca1i | 130.82 (7) |
| O1ii—Ca1—O2iii | 156.06 (8) | O1i—Ca1—Ca1iv | 115.44 (6) |
| O1i—Ca1—O2 | 156.06 (8) | O1ii—Ca1—Ca1iv | 115.44 (6) |
| O1ii—Ca1—O2 | 91.88 (8) | O2iii—Ca1—Ca1iv | 88.51 (6) |
| O2iii—Ca1—O2 | 88.60 (12) | O2—Ca1—Ca1iv | 88.51 (6) |
| O1i—Ca1—O3 | 70.48 (7) | O3—Ca1—Ca1iv | 171.90 (7) |
| O1ii—Ca1—O3 | 70.48 (7) | O3iv—Ca1—Ca1iv | 43.17 (8) |
| O2iii—Ca1—O3 | 85.70 (8) | O1iii—Ca1—Ca1iv | 39.79 (5) |
| O2—Ca1—O3 | 85.70 (8) | O1—Ca1—Ca1iv | 39.79 (5) |
| O1i—Ca1—O3iv | 82.59 (8) | C1iii—Ca1—Ca1iv | 64.56 (7) |
| O1ii—Ca1—O3iv | 82.59 (8) | C1—Ca1—Ca1iv | 64.56 (7) |
| O2iii—Ca1—O3iv | 118.06 (7) | Ca1i—Ca1—Ca1iv | 144.47 (4) |
| O2—Ca1—O3iv | 118.06 (7) | C1—O1—Ca1iv | 154.2 (2) |
| O3—Ca1—O3iv | 144.93 (11) | C1—O1—Ca1 | 91.54 (19) |
| O1i—Ca1—O1iii | 97.25 (7) | Ca1iv—O1—Ca1 | 96.69 (7) |
| O1ii—Ca1—O1iii | 149.97 (5) | C1—O2—Ca1 | 94.01 (18) |
| O2iii—Ca1—O1iii | 52.19 (7) | S1—O3—Ca1 | 139.05 (18) |
| O2—Ca1—O1iii | 101.88 (8) | S1—O3—Ca1i | 127.75 (19) |
| O3—Ca1—O1iii | 136.43 (6) | Ca1—O3—Ca1i | 93.19 (9) |
| O3iv—Ca1—O1iii | 67.37 (7) | O2—C1—O1 | 121.8 (3) |
| O1i—Ca1—O1 | 149.97 (5) | O2—C1—C2 | 120.6 (3) |
| O1ii—Ca1—O1 | 97.25 (7) | O1—C1—C2 | 117.6 (3) |
| O2iii—Ca1—O1 | 101.88 (8) | O2—C1—Ca1 | 60.08 (16) |
| O2—Ca1—O1 | 52.19 (7) | O1—C1—Ca1 | 62.08 (16) |
| O3—Ca1—O1 | 136.43 (6) | C2—C1—Ca1 | 173.4 (2) |
| O3iv—Ca1—O1 | 67.37 (7) | C3—C2—C7 | 118.8 (3) |
| O1iii—Ca1—O1 | 71.78 (10) | C3—C2—C1 | 120.2 (3) |
| O1i—Ca1—C1iii | 93.35 (8) | C7—C2—C1 | 121.1 (3) |
| O1ii—Ca1—C1iii | 170.72 (8) | C4—C3—C2 | 120.4 (3) |
| O2iii—Ca1—C1iii | 25.91 (8) | C4—C3—H3 | 119.8 |
| O2—Ca1—C1iii | 97.39 (9) | C2—C3—H3 | 119.8 |
| O3—Ca1—C1iii | 110.58 (8) | C5—C4—C3 | 120.3 (4) |
| O3iv—Ca1—C1iii | 92.57 (8) | C5—C4—H4 | 119.9 |
| O1iii—Ca1—C1iii | 26.38 (7) | C3—C4—H4 | 119.9 |
| O1—Ca1—C1iii | 88.11 (8) | C6—C5—C4 | 120.2 (4) |
| O1i—Ca1—C1 | 170.72 (8) | C6—C5—H5 | 119.9 |
| O1ii—Ca1—C1 | 93.35 (8) | C4—C5—H5 | 119.9 |
| O2iii—Ca1—C1 | 97.39 (9) | C5—C6—C7 | 119.9 (3) |
| O2—Ca1—C1 | 25.91 (8) | C5—C6—H6 | 120.1 |
| O3—Ca1—C1 | 110.58 (8) | C7—C6—H6 | 120.1 |
| O3iv—Ca1—C1 | 92.57 (8) | C2—C7—C6 | 120.4 (3) |
| O1iii—Ca1—C1 | 88.11 (8) | C2—C7—H7 | 119.8 |
| O1—Ca1—C1 | 26.38 (7) | C6—C7—H7 | 119.8 |
| C1iii—Ca1—C1 | 94.77 (13) | S1—C8—H8A | 109.5 |
| O1i—Ca1—Ca1i | 43.52 (5) | S1—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| O1ii—Ca1—Ca1i | 43.52 (5) | H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| O2iii—Ca1—Ca1i | 115.90 (7) | S1—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| O2—Ca1—Ca1i | 115.90 (7) | H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| O3—Ca1—Ca1i | 43.63 (7) | H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| O3iv—Ca1—Ca1i | 101.29 (8) | O3—S1—C8iii | 105.78 (14) |
| O1iii—Ca1—Ca1i | 140.76 (5) | O3—S1—C8 | 105.78 (14) |
| O1—Ca1—Ca1i | 140.76 (5) | C8iii—S1—C8 | 98.4 (3) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y, z+1/2; (ii) x, −y, z+1/2; (iii) −x+1, y, z; (iv) −x+1, −y, z−1/2.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg is the centroid of the benzoate ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C8—H8A···Cg | 0.96 | 2.84 | 3.790 (4) | 169 |
References
- Allmann, R. (1975). Monatsh. Chem. 106, 779–793.
- Altomare, A., Cascarano, G., Giacovazzo, C. & Guagliardi, A. (1993). J. Appl. Cryst. 26, 343–350.
- Azizov, O., Kadirova, Z., Azizov, T., Tolipov, S. & Ibragimov, B. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, m597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Babich, O. A., Kokozay, N. V. & Pavlenko, V. A. (1996). Polyhedron, 15, 2727–2731.
- Blessing, R. H. (1995). Acta Cryst. A51, 33–38. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Brandenburg, K. & Putz, H. (2006). DIAMOND. Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Busskamp, H., Deacon, G. B., Hilder, M., Junk, P. C., Kynast, U. H., Lee, W. & Turner, D. R. (2007). CrystEngComm, 9, 394–411.
- Buvaylo, E. A., Kokozay, V. N., Vassilyeva, O. Yu., Skelton, B. W., Jezierska, J., Brunel, L. C. & Ozarowski, A. (2005). Chem. Commun. pp. 4976–4978. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Coxall, R. A., Harris, S. G., Henderson, D. K., Parsons, S., Tasker, P. A. & Winpenny, R. E. P. (2000). J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. pp. 2349–2356.
- Deacon, G. B., Hein, S., Junk, P. C., Jüstel, T., Lee, W. & Turner, D. R. (2007). CrystEngComm, 9, 1110–1123.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Groom, C. R. & Allen, F. H. (2014). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 662–671. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Parsons, S., Flack, H. D. & Wagner, T. (2013). Acta Cryst. B69, 249–259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Rigaku (1999). CrystalClear. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Senkovska, I. & Thewalt, U. (2005). Acta Cryst. C61, m448–m449. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Vassilyeva, O. Yu., Kokozay, V. N., Zhukova, N. I. & Kovbasyuk, L. A. (1997). Polyhedron, 16, 263–266.
- Yano, S., Numata, M., Kato, M., Motoo, S. & Nishimura, T. (2001). Acta Cryst. E57, m488–m490.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015012487/zs2334sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015012487/zs2334Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 1409468
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report






