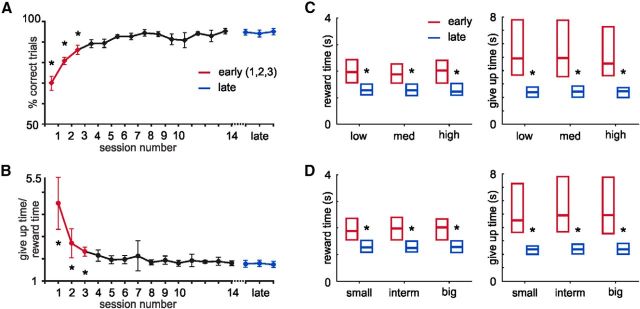
Figure 2.
Performance in the behavioral task. A, Percentage of trials successfully completed increases with training. *p < 0.01 (Tukey post hoc, repeated-measures ANOVA). B, Behavioral report of reward time measured as the ratio between the time in which the animal exits the nose-poke in unrewarded trials (give up time) relative to the reward delivery time per session. A, B, Sessions classified as early and late in training are plotted in red and blue, respectively. *p < 0.05 (Tukey post hoc, repeated-measures ANOVA). There was no difference in the reward time or give up time for the different light intensities (C) or reward magnitudes (D) in either early or late training. Training did shorten both the reward and give up times. *p < 0.05 (two-way repeated-measures ANOVA).