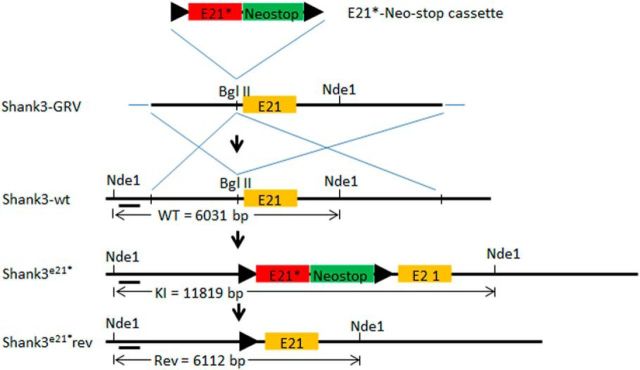
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the exon 21 insertion mutation (insert G) mouse model. A gene repair targeting vector (Shank3-GRV) was created via insertion of an insertion mutant exon 21 followed by a NeoStop cassette flanked by loxP sites (“floxed” E21G-NeoStop cassette) upstream of the wild-type exon 21. The resulting Shank3-GRV was targeted in mouse ES cells into the wild-type Shank3 gene (Shank3-wt). This resulted in the creation of mice constitutively expressing a human Shank3 exon 21 insertion mutation associated with autism, the Shank3G mouse model. In future experiments, the Shank3G mice can be genetically reversed to wild-type Shank3 whenever and wherever cre-recombinase is activated or expressed. Nde1 denotes restriction sites with size of diagnostic restriction fragments indicated between the Nde1 sites below.