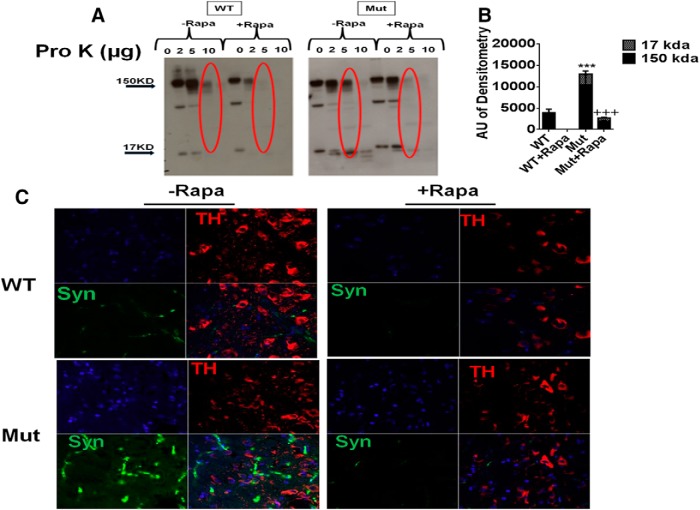
Figure 2.
Increased levels of pro-K-insoluble α-synuclein in parkin Q311X mutants are abrogated by rapamycin feeding. A, Striatal tissue lysates from parkin mutant mice (Mut) versus WT littermate controls on control or rapamycin diet (Rapa) were incubated with 0–10 μg/ml pro-K and run on Western blots probed with antibody against α-synuclein. B, Densometric quantitation of monomeric (∼17 kDa) versus large oligomeric (∼150 kDa) α-synuclein levels in 5 μg/ml pro-K-treated samples (red circled on Western blot). ***p < 0.001 versus WT. +++p < 0.001 versus Mut. Three separate experiments were performed in triplicate. C, Representative confocal SN immunocytochemistry from Mut versus WT littermates on control or Rapa diet treated with 5 μg/ml pro-K (Lu et al., 2009) and probed with antibody against TH (red) or α-synuclein (Syn, green). Blue represents nuclear DAPI staining. Original magnification, ×63.