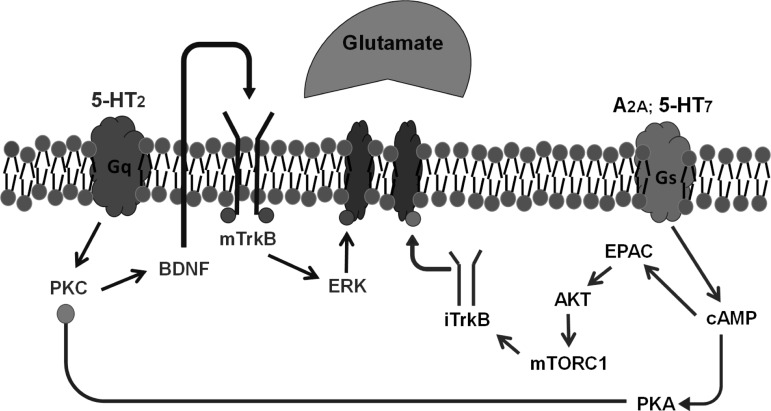
Fig. 3.
Working model of convergent pLTF pathways. The Q pathway to phrenic motor facilitation (pMF) is initiated by episodic activation of Gq protein-coupled 5-HT2 receptors (MacFarlane and Mitchell 2009; MacFarlane et al. 2011) followed by PKCθ activation (Devinney et al. 2015), new brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) synthesis (Baker-Herman et al. 2004), TrkB (Baker-Herman et al. 2004; Dale EA and Mitchell GS, unpublished observations), and ERK/MAP kinase activation (Hoffman et al. 2012). The mechanism whereby ERK elicits pLTF remains unknown. We propose a newly organized “S” pathway (right) to pLTF initiated by adenosine 2A (A2A) receptors (Golder et al. 2008), followed by cAMP production, EPAC, Akt, and mTOR activation (Fields et al. 2015) and new synthesis of immature TrkB isoforms (Golder et al. 2008). Mechanisms downstream of iTrkB are unknown. S-to-Q pathway inhibition via PKA (Hoffman and Mitchell 2013) diverges at cAMP based on recent observations (Fields et al. 2015).