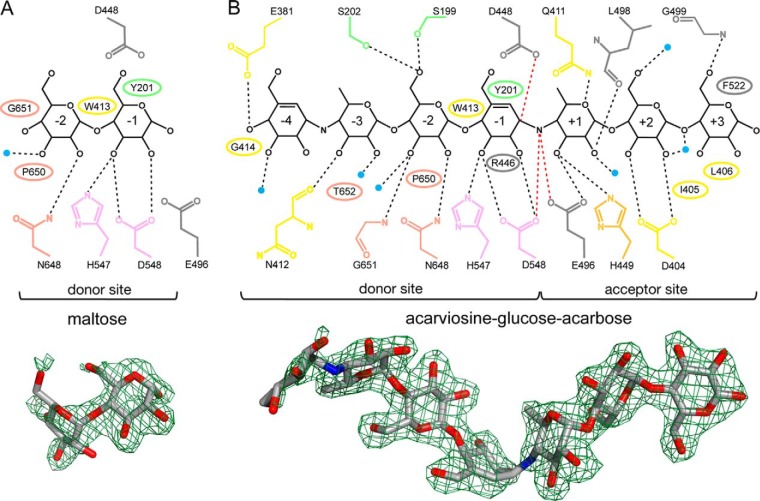
FIGURE 3.
Ligand interactions in the MalQ·maltose (A) and MalQ·AGA complexes (B). Schematic representations of the ligands (black) and all interacting residues (colored as in Fig. 2). MalQ residues that form hydrogen bonds or van der Waals contacts with the respective ligand are indicated as sticks and ellipses, respectively. Water molecules that interact with both the ligand and the protein are depicted as small blue spheres. Numbers inside the sugar rings label the corresponding subsites. Contacts between the sugar substrate and the nucleophilic side chain of Asp-448 (2.6 Å), the acid/base catalyst Glu-496 (2.9 Å), and the putative transition state stabilizer Asp-548 (3.0 Å) are highlighted as red dashed lines. In the MalQ·maltose structure these residues are too far apart (Asp-448, 4.2 Å; Glu-496, 6.0 Å) for contact formation with the substrate. Illustration of the omit FO − FC electron density map (green mesh; contoured at 2.0 and 3.0 σ for maltose and AGA, respectively) with superimposed ligand (stick model) is depicted underneath.