FIGURE 4.
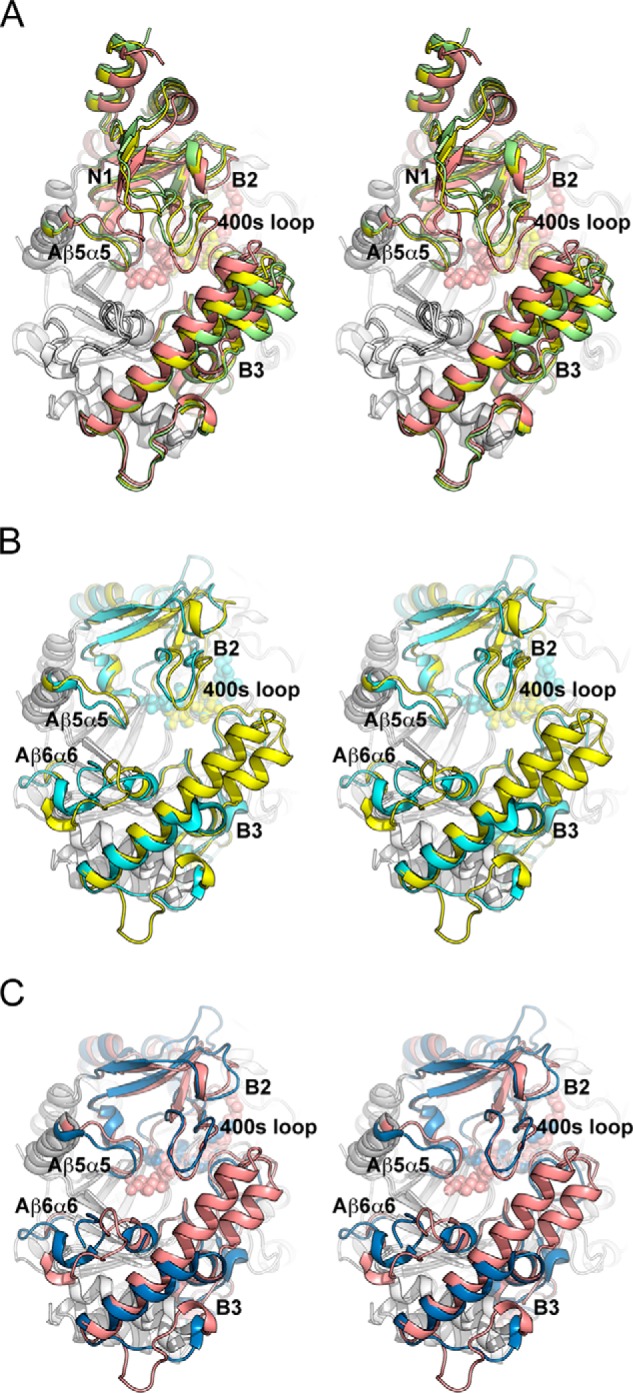
Structural comparison (stereo view) of MalQ with amylomaltase from Thermus sp. A, superposition of the MalQ structures in schematic representation as follows: apo-MalQ (green), MalQ·maltose (yellow), and MalQ·AGA (salmon). Subdomain N2 was omitted for clarity. B, superposition of MalQ·maltose (yellow) and amylomaltase from T. aquaticus (PDB code 1ESW, cyan) (40). Subdomains N1 and N2 of MalQ are not depicted, due to their absence in the Thermus structures. C, similar superposition of MalQ·AGA (salmon) and the amylomaltase of T. thermophilus (PDB code 2OWW, blue) (19). For superposition, the 36 Cα positions of the eight β-strands within the central TIM barrel were used, corresponding to residues 143–148, 181–184, 370–375, 444–447, 492–495, 516–519, 540–543, and 632–635 of MalQ. Ligands are shown as spheres in the same color as the schematics.
