FIGURE 8.
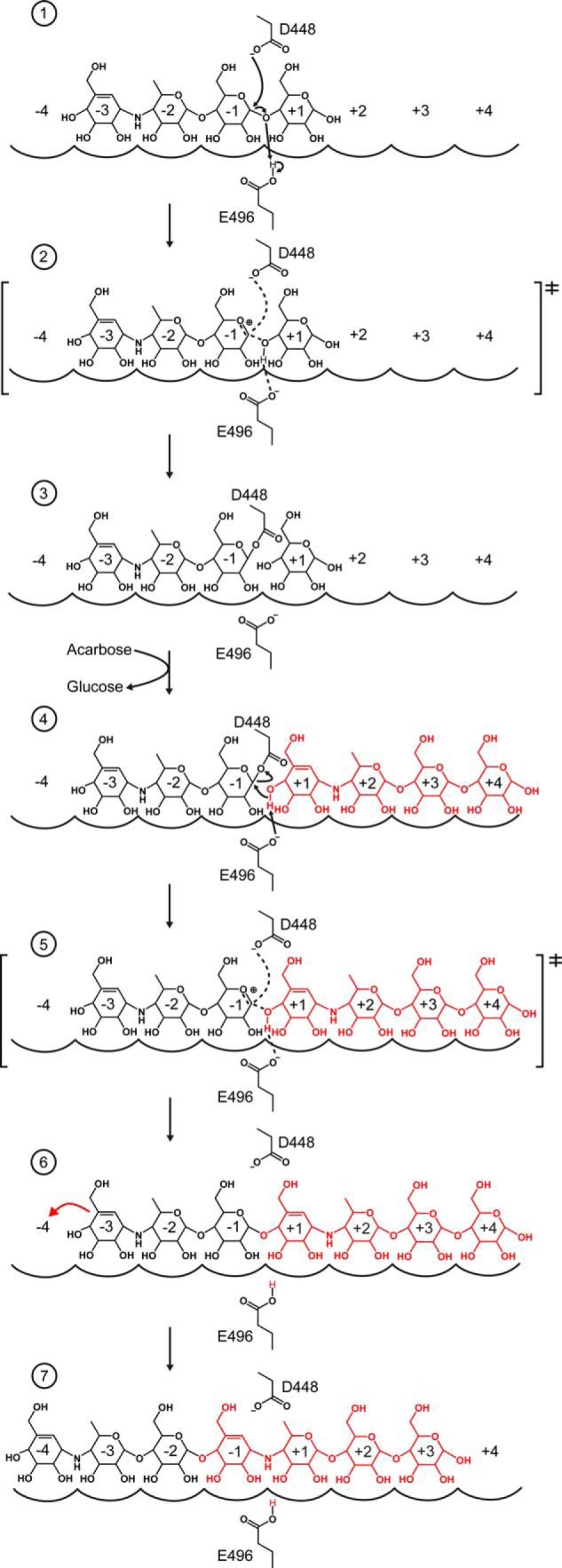
Mechanism of MalQ inhibition by acarbose. The two acarbose molecules that are converted to AGA by MalQ are colored black and red. MalQ subsites are indicated by arches and numbered −4 to +4. The catalytic residues Asp-448 and Glu-496 are shown as sticks. The reaction proceeds in seven stages (see text), each shown in one panel, which can be deduced from distinct crystal structures. Panel 1, MalQ·maltose and TaAM·acarbose (PDB code 1ESW); panel 2, MalQ·AGA; panels 3 and 4, TtAM·AG and TtAM·AG·4G (PDB codes 2OWC and 2OWW); panel 5, MalQ·AGA; panel 6, MalQ·maltose and TaAM·acarbose (PDB code 1ESW); and panel 7, MalQ·AGA.
