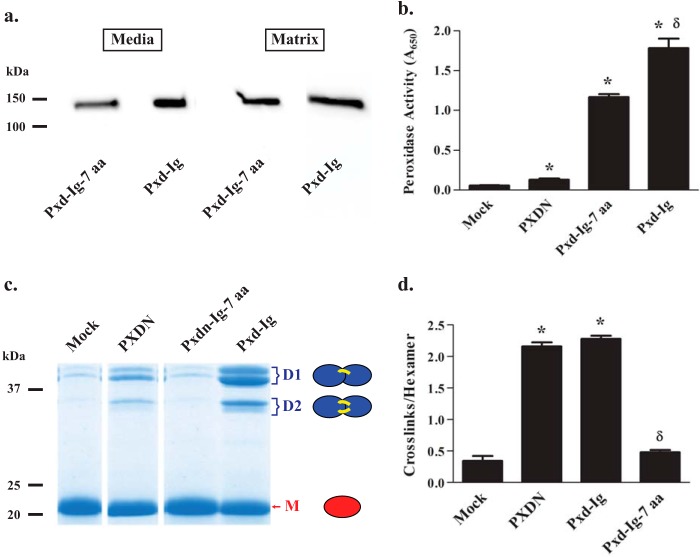
FIGURE 5.
The N-terminal 7 residues of the peroxidasin immunoglobulin domains are necessary to cross-link collagen IV. a, immunoblotting, under reducing conditions, reveals the deletion construct lacking 7 N-terminal amino acids from the first immunoglobulin domain (Pxd-Ig-7 aa) is adequately expressed in cell culture media and incorporated into matrix. Blots are representative of 3 independent experiments. b, Pxd-Ig-7 aa demonstrates tetramethylbenzidine oxidation greater than full-length peroxidasin, but slightly less than the peroxidase-immunoglobulin construct (Pxd-Ig; ANOVA followed by post-hoc Tukey's pairwise comparison; *, p < 0.05 compared with PXDN; δ, p < 0.05 Pxd-Ig-7 aa versus Pxd-Ig, n = 3). c, SDS-PAGE of NC1 hexamers (non-reducing conditions) isolated after overlay with mock, PXDN, Pxd-Ig-7 aa, and Pxd-Ig reveal the formation of cross-linked dimeric subunits (D1 and D2 representing single and double cross-linked forms, respectively) primarily with PXDN and Pxd-Ig, whereas mock and Pxd-Ig-7 aa exhibit primarily monomeric, uncross-linked subunits (M). Each of these band regions (D1, D2, and M) appear as single bands (arrows) or doublets (brackets) due to unidentified variability in electrophoretic migration (4, 26, 27). d, the number of cross-links per collagen IV NC1 hexamer was determined for mock, PXDN, Pxd-Ig-7 aa, and Pxd-Ig-transfected cells using densitometric quantitation of the dimeric and monomeric subunits from SDS-PAGE of collagenase-digested PFHR-9 matrix as shown in c. Data were analyzed using analysis of variance followed by post hoc pairwise comparisons with Tukey's correction for multiple comparisons (*, p < 0.05 compared with mock; δ, p < 0.05 compared with PXDN, n = 3).