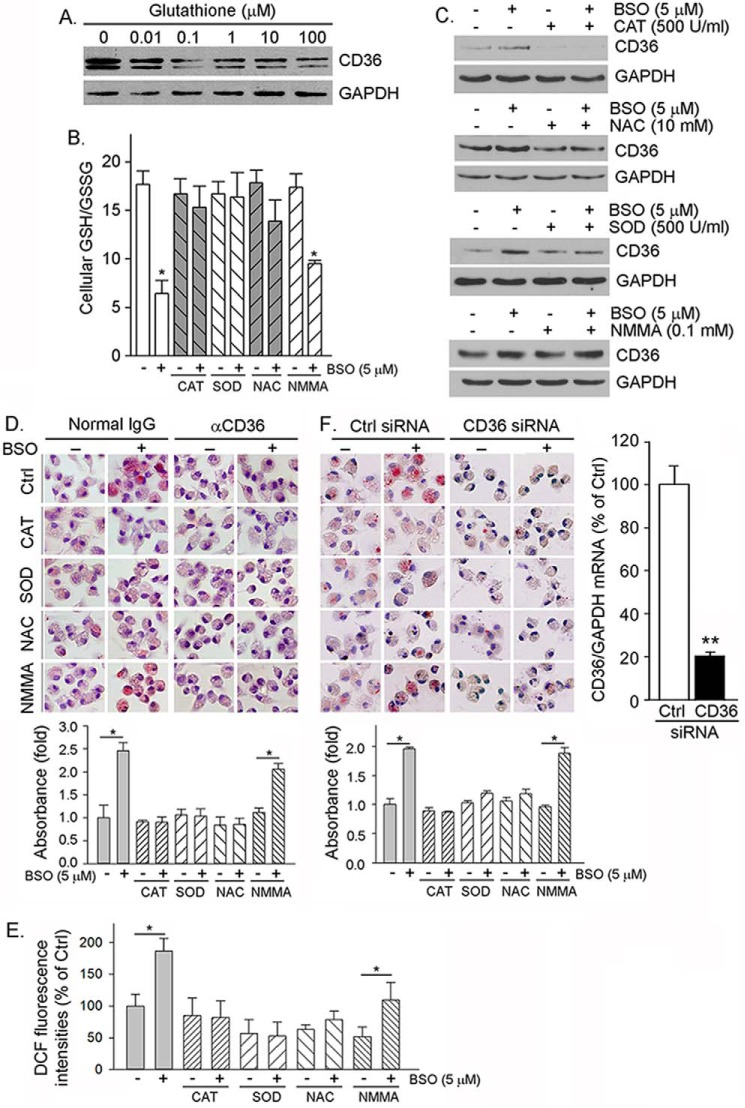
FIGURE 3.
Cellular GSH/GSSG status regulates macrophage CD36 expression and oxLDL uptake. A, RAW264.7 cells were treated with GSH at the indicated concentrations for 16 h followed by determination of CD36 protein expression. B and C, mouse peritoneal macrophages were treated with CAT, NAC, SOD, and NMMA alone or each plus BSO as indicated for 16 h. After treatment, cells were used to determine GSH/GSSG (B, *, p < 0.05 versus control (n = 3)) and CD36 expression (C). D, peritoneal macrophages were treated with CAT, SOD, NAC, and NMMA or each plus BSO as indicated for 16 h. After treatment, cells were used to determine cellular oxLDL uptake by incubation with oxLDL in the presence of normal IgG (left panel) and anti-CD36 antibody (right panel) followed by Oil Red O staining, extraction, and quantitation of the accumulated Oil Red O dye within cells. *, p < 0.05 (n = 3). E, the cells in Fig. 3D were also determined ROS production by assay kit. *, p < 0.05 (n = 3). DCF, dichlorofluorescein. F, peritoneal macrophages were transfected with scrambled siRNA (Ctrl siRNA) or CD36 siRNA (50 nm of each) and then treated with CAT, SOD, NAC, and NMMA alone or each plus BSO. Inhibition of CD36 expression was determined by real time RT-PCR (right panel). **, p < 0.01 (n = 3). Cellular oxLDL uptake and foam cell formation were determined by incubation with oxLDL followed by Oil Red O staining (left and middle panels) and quantitation of accumulated Oil Red O dye within cells. *, p < 0.05 (n = 3).