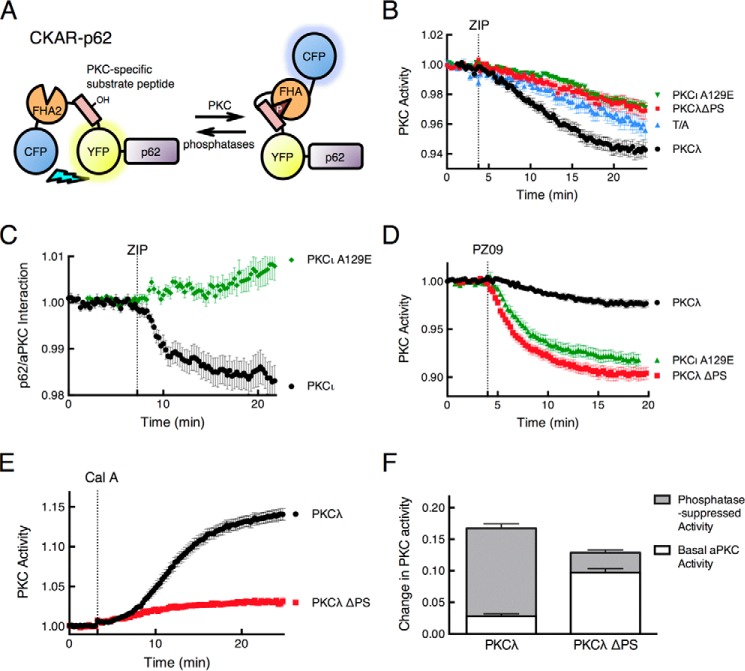
FIGURE 4.
ZIP releases the pseudosubstrate of PKCλ from p62 to allow intramolecular autoinhibition of the kinase. A, schematic showing fusion of the PKC activity reporter CKAR to the N terminus of p62. Phosphorylation causes an intramolecular clamp of the phosphorylated segment (pink) with a phospho-peptide-binding FHA2 module (orange) that results in a decrease in FRET between the flanking CFP (blue) and YFP (yellow) (see Ref. 33 for more details). B, COS-7 cells co-expressing CKAR-p62 and mCherry-tagged wild-type PKCλ (black circles, n = 44), PKCλ ΔPS (red squares, n = 19), or PKCι A129E (green triangles, n = 41) were pretreated with 1 μm Gö6983, an inhibitor of conventional and novel PKC isozymes, and then monitored for CFP/FRET ratio changes following 5 μm ZIP treatment. The control CKAR-p62 T/A (blue triangles, n = 23), where its phospho-acceptor Thr was mutated to Ala, was also examined under the same experimental conditions. Data were plotted as PKC activity and represent the normalized FRET/CFP ratio mean ± S.E. of the indicated number of cells from at least 3 independent experiments. C, the FRET/CFP ratio of COS-7 cells co-expressing CFP-p62 and YFP-PKCι (black circles, n = 31) or YFP-PKCι A129E (green diamonds, n = 28) was monitored before and after 5 μm ZIP treatment. Data were plotted as a p62-aPKC interaction and represent the normalized FRET/CFP ratio mean ± S.E. of the indicated number of cells from at least 3 independent experiments. D, COS-7 cells co-expressing CKAR-p62 and mCherry-tagged wild-type PKCλ (black circles, n = 28), PKCλ ΔPS (red squares, n = 30), or PKCι A129E (green triangles, n = 18) were monitored for CFP/FRET ratio changes before and after treatment with 5 μm PZ09, an atypical PKC-selective inhibitor (48). E, COS-7 cells co-expressing CKAR-p62 and either mCherry-tagged wild-type PKCλ (black circles, n = 33) or PKCλ ΔPS (red squares, n = 38) were monitored for CFP/FRET ratio changes when treated with 50 nm calyculin A, a Ser/Thr protein phosphatase inhibitor (56). Data were plotted as PKC activity and represent the normalized FRET/CFP ratio mean ± S.E. of the indicated number of cells from at least 3 independent experiments. F, quantification of basal and phosphatase-suppressed activities of PKCλ and PKCλ ΔPS was calculated as a fraction of FRET ratio change. The data were extrapolated from the plateau portion of the curves in panels D and E, 20 min after the addition of PZ09 or calyculin A.