FIGURE 4.
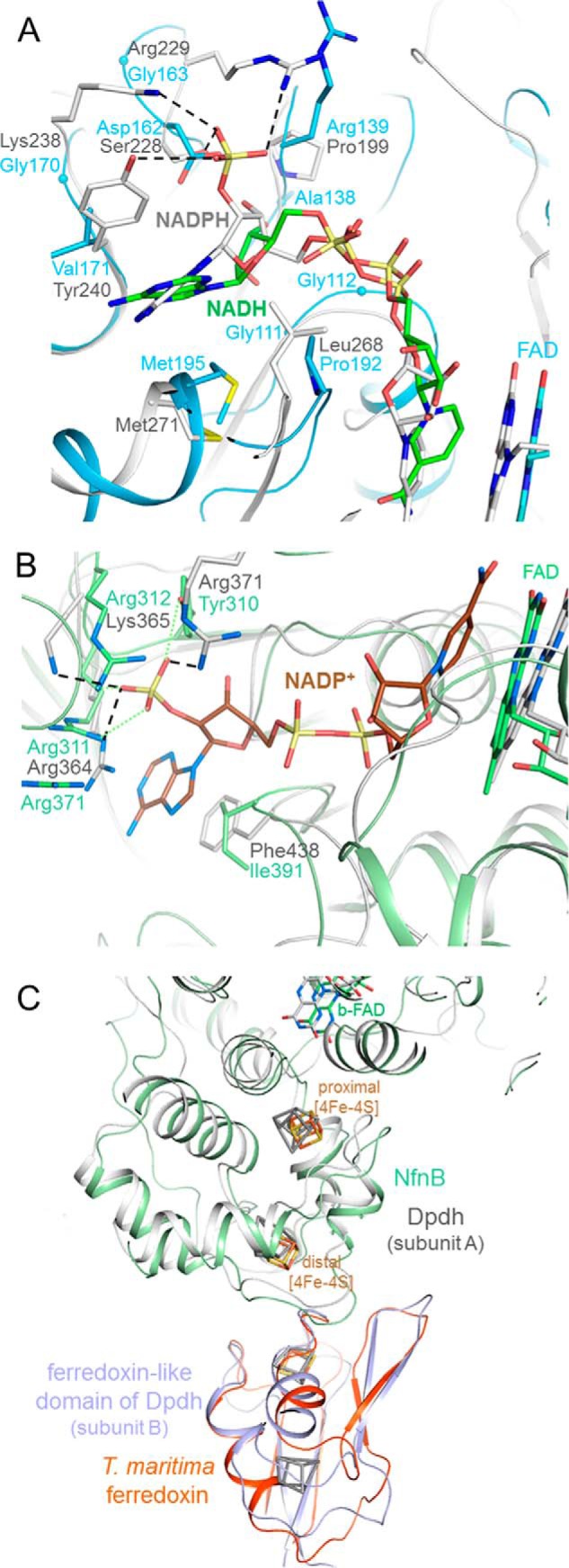
Substrate binding sites of the NfnAB complex. A, NADH (carbon in green) is bound to NfnA (deep sky blue) at the C-terminal side of the central β-sheet of the NAD domain. The different adenosine binding sites in NfnAB and Fnr are highlighted by superimposing the NfnAB-NADH and the Fnr-NADPH complex structures. A hypothetical 2-phosphate group of NADPH in NfnAB would sterically and electrostatically interfere with Asp162 and is not surrounded by positively charged residues as in Fnr. B, modeled NADP+ bound to NfnB. The superimposed NADP binding domains of the Dpdh-NADP+ complex (gray) and NfnAB (green) reveal a highly conserved site for binding NADP(H) (carbons in brown) and not NAD(H). C, binding of ferredoxin. Ferredoxin (orange-red) is modeled close to the distal [4Fe-4S] cluster of NfnB based on the structure of Dpdh, which contains both a NfnB-like and a ferredoxin-like domain (gray and blue). Its iron-sulfur clusters are drawn in gray.
