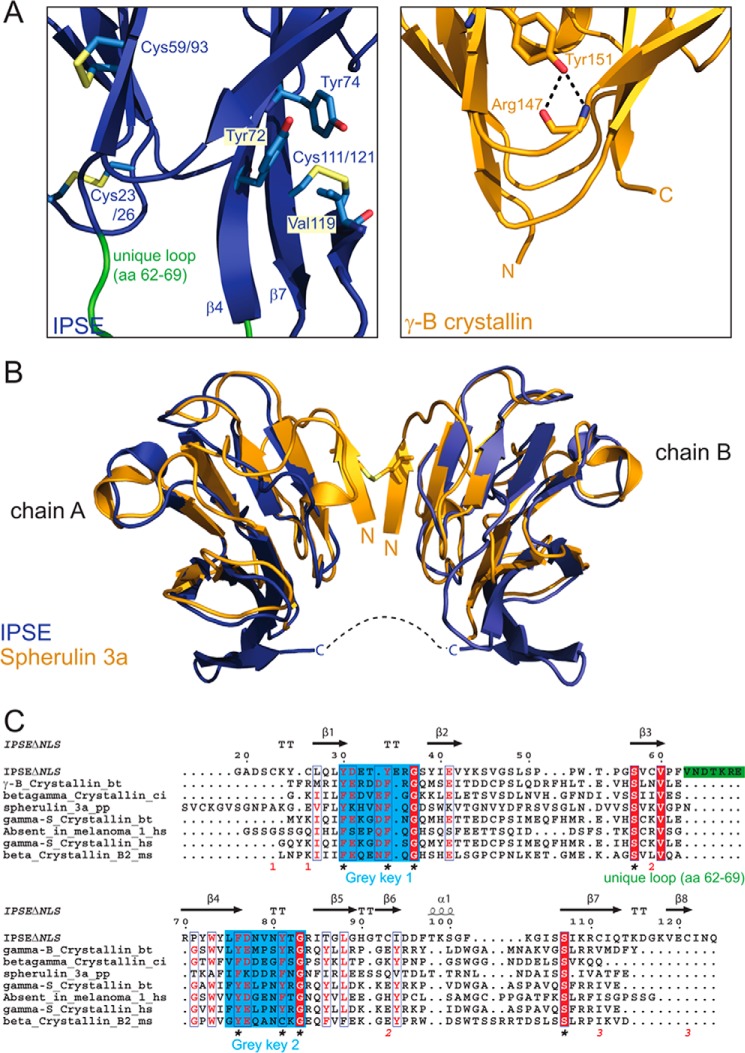
FIGURE 3.
IPSEΔNLS adopts a βγ-crystallin fold. A, zoomed view of IPSEΔNLS (blue, right) and human eye lens γ-B-crystallin (dark yellow, left). Shown are the residues of the tyrosine corner of γ-B-crystallin (Tyr-151 and Arg-147) and the orthogonal stacked Tyr-72 and -74 as well as the disulfide bridges of IPSEΔNLS (sticks) and the flexible loop (amino acids (aa) 62–69) (green). B, structure superposition of two IPSEΔNLS monomers (blue) with dimeric Spherulin 3A (orange). Structures align with a backbone r.m.s.d. of 1.8 Å. C, structure-based multiple sequence alignment of crystallin superfamily members. Above the sequences: secondary structure elements of IPSEΔNLS (except of disulfide bridges). Below the sequences: disulfide bridges are shown as red numbers; the flexible loop (amino acids 62–69) unique to IPSE/α-1 is depicted as a green bar; the two (F/Y)XXXX(F/Y)G signature sequences and the conserved serine residues characteristic of the crystallin fold are indicated by asterisks.