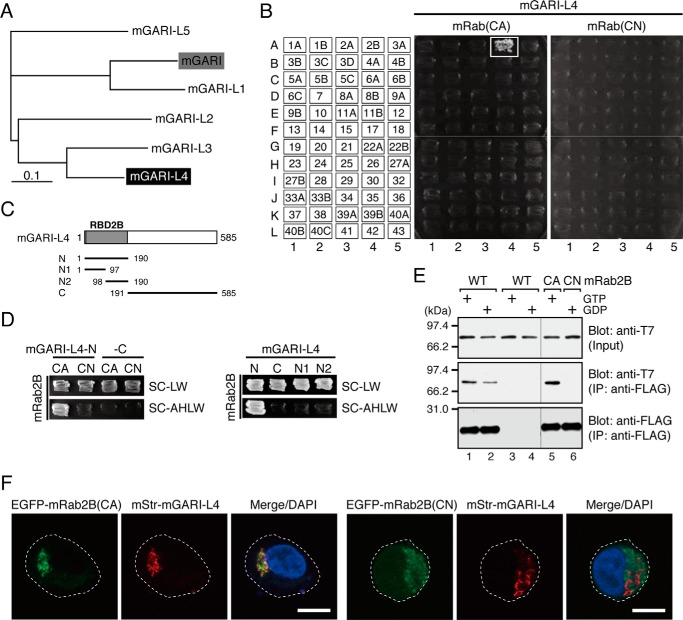
FIGURE 6.
GARI-L4 is a novel Rab2B-specific binding protein in the Golgi. A, phylogenetic relationships between mouse GARI (shaded box) and its related proteins, GARI-L1–5. GARI-L4, on which we focused in this study, is shown against a black background. The phylogenetic tree was drawn by using the ClustalW program set at the default parameters. B, specific interaction between GARI-L4 and Rab2B(CA) as revealed by yeast two-hybrid assays. The assays were performed as described previously (22, 33, 34). Yeast cells containing pGAD-C1-GARI-L4 and pGBD-C1-Rabs(CA/CN)ΔCys (34) were streaked on synthetic complete medium lacking adenine, histidine, leucine, and tryptophan (selection medium) and incubated at 30 °C for 1 week. A positive patch is represented by a white box. C, schematic representation of the truncated mutants of mouse GARI-L4 used in this study. The N-terminal 190 amino acids of GARI-L4 showed high similarity to the N-terminal domain of GARI (22) and were found to function as a Rab-binding domain specific for Rab2B (RBD2B) (see D). D, mapping of the site responsible for Rab2B binding in mouse GARI-L4. Interaction between GARI-L4 mutants (in C) and Rab2B(CA/CN) was assessed by yeast two-hybrid assays as described in B. Yeast cells containing pGAD-C1-GARI-L4 mutants and pGBD-C1-Rab2B(CA/CN)ΔCys (34) were streaked on synthetic complete medium lacking leucine and tryptophan (SC-LW) and synthetic complete medium lacking adenine, histidine, leucine, and tryptophan (selection medium; SC-AHLW) and incubated at 30 °C for 1 day and 1 week, respectively. E, GTP-dependent interaction between T7-tagged mouse GARI-L4 and FLAG-tagged mouse Rab2B (WT/CA/CN) in cultured mammalian cells. Co-immunoprecipitation assays in COS-7 cells were performed as described previously (29, 37). F, co-localization of mouse GARI-L4 with Rab2B(CA), but not with Rab2B(CN), in HeLa-S3 cells. HeLa-S3 cells were co-transfected with pmStr-C1-mGARI-L4 and pEGFP-C1-mRab2B(CA or CN) and then analyzed by confocal fluorescence microscopy. Scale bars, 20 μm.