FIGURE 4.
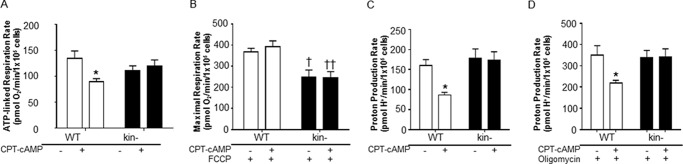
CPT-cAMP/PKA regulates cellular bioenergetics. CPT-cAMP decreases ATP-linked respiration (A), and PKA is necessary to drive ATP synthesis in the presence of the protonophore FCCP (stimulating maximal activity of the electron transport chain) (B). Cells were incubated with 8 mm glucose, 1 mm pyruvate, and 3 mm glutamine in unbuffered DMEM. C, medium acidification can serve as an indirect measure of glycolytic turnover as catabolism of a molecule of uncharged glucose into two molecules of lactate (pKa 3.9) requires the release of two protons at physiological pH. Stimulation of PKA with CPT-cAMP in WT cells decreased proton production. D, a similar effect of CPT-cAMP on WT cells occurs when the mitochondrial ATP synthase is blocked by Oligomycin. Cells were incubated with 8 mm glucose, 1 mm pyruvate, and 3 mm glutamine in unbuffered DMEM. All data are the mean ± S.E. (n≥3), * = p < 0.05 versus control, † = p < 0.05 versus WT control, †† = p < 0.01 versus WT +CPT-cAMP.
