Fig. 3.
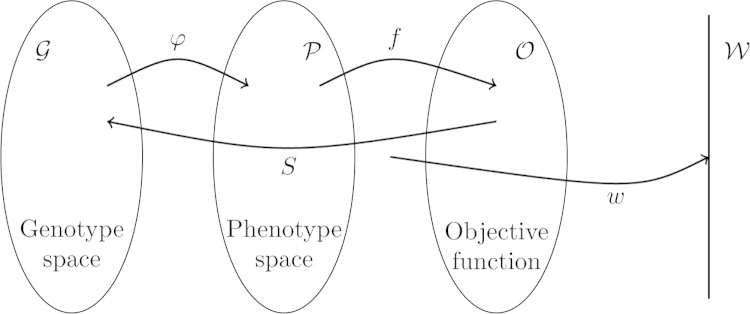
A basic sequence of operations leading to a selectable population. A population distributed over the genotype space is assigned phenotype values via the genotype–phenotype mapping , which are then interpreted by f into objective function values . Variation operators generate new variation at the genotypic level and selection operators act at the level of the objective function, generating a new population in . The line represents the probability for this individual to be present in the next generation, which is a consequence of the selection operators used. This is typically called “fitness” in PG and is related to the reproductive rate in EC.
