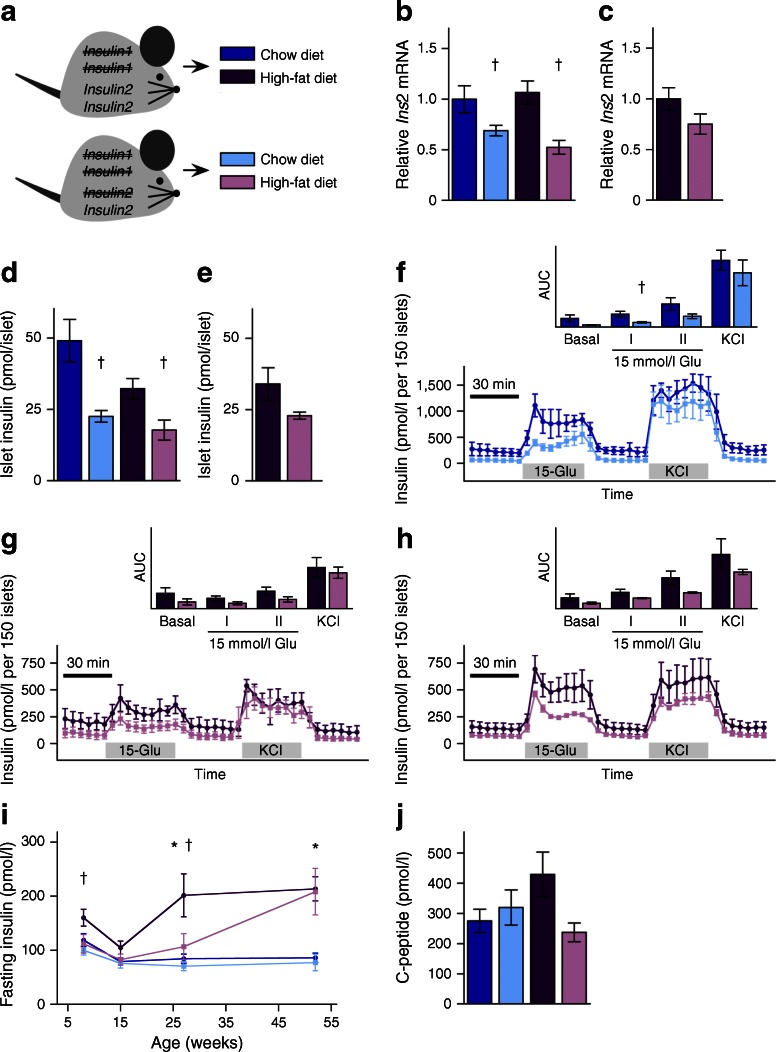
Fig. 1.
Transiently attenuated HFD-induced hyperinsulinaemia in Ins1 −/−:Ins2 +/− mice. (a) Experimental design of Ins1 −/−:Ins2 +/+ and Ins1 −/−:Ins2 +/− littermates fed CD or HFD. (b, c) Islet Ins2 mRNA is corrected against β-actin mRNA and normalised to CD-fed Ins1 −/−:Ins2 +/+ mice at 25 weeks (n = 3–5) (b), or HFD-fed Ins1 −/−:Ins2 +/+ mice at 50 weeks (n = 3) (c). (d, e) Insulin content in islets from mice at 25 (d) and 50 weeks (e). (f–h) At 25 (f, g) and 50 weeks (h), insulin secretion by 150 islets perifused with basal 3 mmol/l glucose followed by stimulatory 15 mmol/l glucose (Glu) or 30 mmol/l KCl, with AUC (insets; y-axis units, pmol/l × min) depicted, including phases I/II of glucose stimulation (n = 3). (i, j) Fasted insulin (n = 17–21) (i) and C-peptide (n = 5–6) (j) at 27 weeks is from in vivo sampling. Dark blue, CD-fed Ins1 −/−:Ins2 +/+ mice; dark purple, HFD-fed Ins1 −/−:Ins2 +/+ mice; light blue, CD-fed Ins1 −/−:Ins2 +/− mice; light purple, HFD-fed Ins1 −/−:Ins2 +/− mice. Data are means ± SEM. *p ≤ 0.05, CD vs HFD; † p ≤ 0.05, Ins1 −/−:Ins2 +/+ vs Ins1 −/−:Ins2 +/−