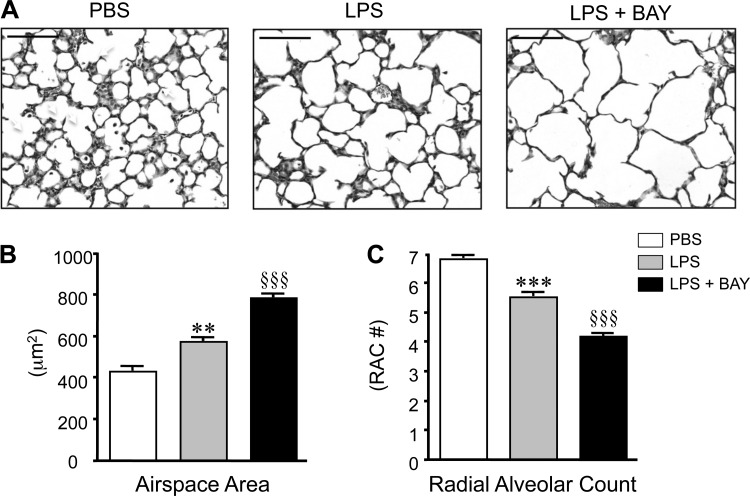
Fig. 1.
Systemic lipopolysaccharide (LPS) disrupts distal lung growth in the early alveolar lung, and inhibiting the NF-κB pathway accentuates these detrimental effects. A: representative images of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained lung sections obtained from postnatal day 7 (P7) mice, 24 h after administration of vehicle (PBS), LPS, or LPS + BAY 11-7082 (LPS + BAY). B: morphometric analysis to determine the distal airspace area, with **P < 0.01 vs. PBS and §§§P < 0.001 vs. PBS and LPS. C: morphometric analysis to determine the radial alveolar count, with ***P < 0.001 vs. PBS and §§§P < 0.001 vs. PBS and LPS. All data are expressed as means ± SE, with n = 6–9 animals per group. Scale bar = 100 μm. RAC, radial alveolar count.