Fig. 2.
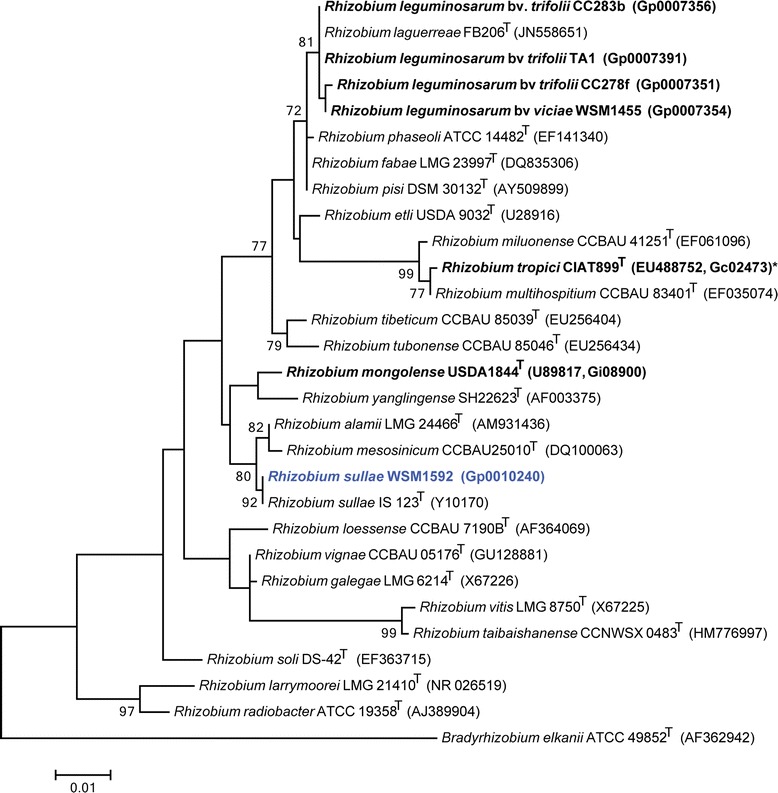
Phylogenetic tree highlighting the position of R. sullae strain WSM1592 (shown in blue print) relative to other type and non-type rhizobia strains using a 901 bp internal region of the 16S rRNA gene. Bradyrhizobium elkanii ATCC 49852T was used as an outgroup. All sites were informative and there were no gap-containing sites. Phylogenetic analyses were performed using MEGA, version 5.05 [33]. The tree was built using the maximum likelihood method with the General Time Reversible model. Bootstrap analysis with 500 replicates was performed to assess the support of the clusters. Type strains are indicated with a superscript T. Strains with a genome sequencing project registered in GOLD [18] have the GOLD ID mentioned after the strain number and represented in bold, otherwise the NCBI accession number is provided. Finished genomes are designated with an asterisk
