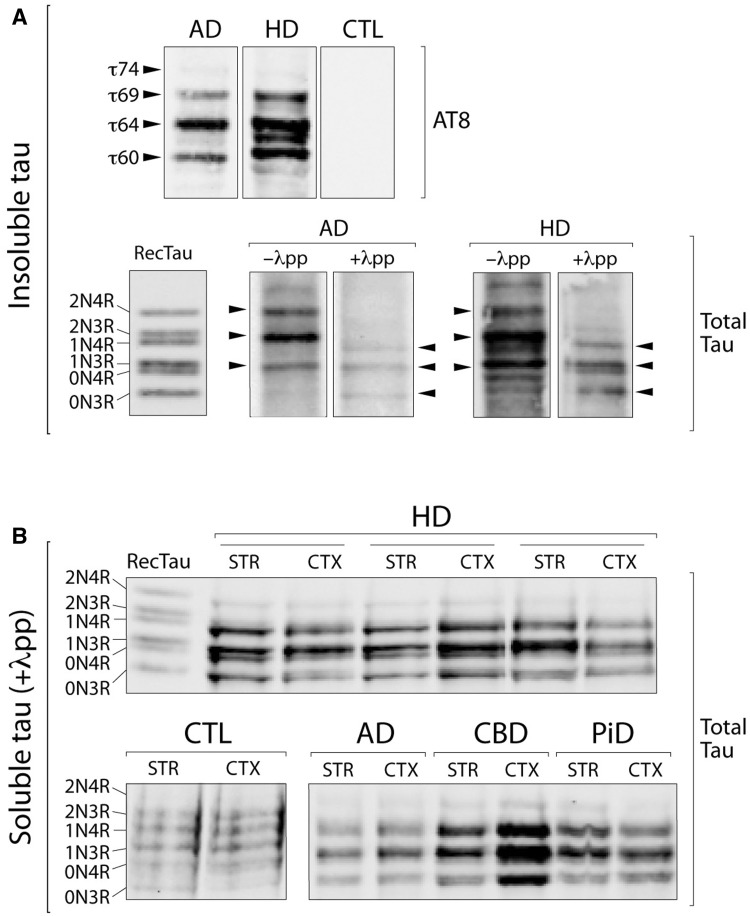
Figure 2.
Biochemical characterization of sarkosyl-insoluble and soluble tau in Huntington’s disease brains. (A) Western blot analysis of the sarkosyl-insoluble tau fraction, before and after dephosphorylation with alkaline phosphatase (λpp), with the AT8 and a total tau antibody in cortical and striatal Huntington’s disease tissues compared to Alzheimer’s disease (AD) cases and healthy controls (CTL). (B) Western blot analysis of the soluble tau fraction after dephosphorylation with alkaline phosphatase (λpp) with a total tau antibody in cortical (CTX) and striatal (STR) Huntington’s disease tissues, compared to a range of tauopathies (CBD = corticobasal degeneration; PiD = Pick’s disease) and healthy controls. RecTau molecular weight (kDa): 2N4R (45.9), 2N3R (42.6), 1N4R (42.9), 1N3R (39.7), 0N4R (40.0), 0N3R (36.8).