Figure 2.
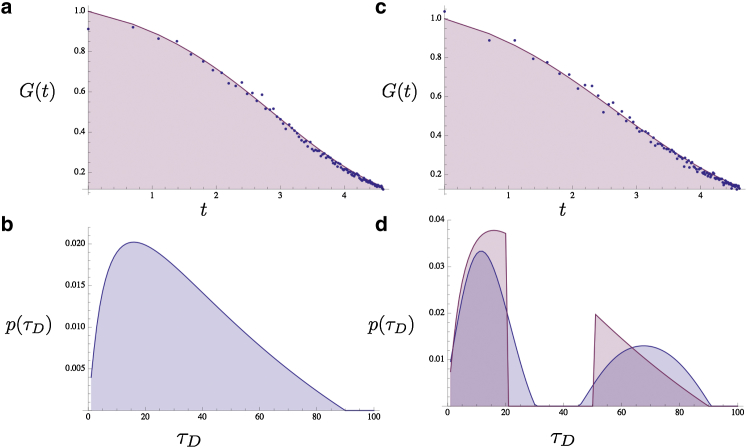
Protein binding sites of different affinities can give rise to apparent anomalous diffusion. A theoretical G(t) (containing 150 points) was created from an anomalous diffusion model, Eq. 3, with α = 0.9, to which 5% white noise was added (a, blue dots, logarithmic in time). In (b), a p(τD) is extracted from this G(t) and, as a check, we used it to reproduce the G(t) (a: solid curve). Part of p(τD) is then excised, which yields a new, to our knowledge, p(τD) (d: pink curve). A G(t) is created from this theoretical distribution with 8% white noise (c: blue dots, logarithmic in time). A p(τD) is then extracted from this (d, blue curve) and the G(t) is reconstructed from this p(τD) as a check (c, solid curve). Time is in arbitrary units. To see this figure in color, go online.