Figure 3.
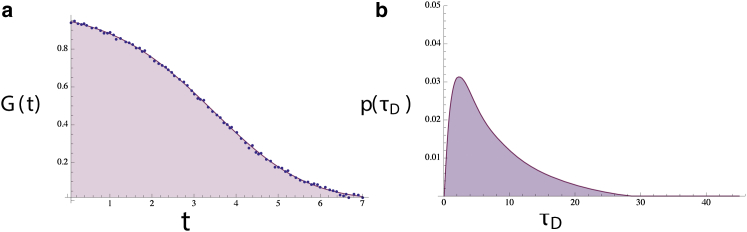
G(t) s may arise from unusual p(τD) distributions that cannot easily be fit using anomalous diffusion models. A skewed-normal distribution (b) plus 6% added noise was used to generate a 100 point G(t) (a, blue dots, equidistant in time). The p(τD) was then extracted (b) and used to reconstruct the noiseless G(t) (a, solid curve). The original and extracted p(τD) are indistinguishable, although agreement of our reconstructed G(t) with the original noisy G(t) is excellent at this noise level. To see this figure in color, go online.
